Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

Grade B of ASTM A 53 is more popular than other grades. These pipes can be bare pipes without any coating, or they may be Hot-Dipped or Zinc-Coated and manufactured by Welding or by a Seamless manufacturing process. In Oil and Gas, A53 grade pipes are used in structural and non-critical applications.
Grade B of ASTM A 53 is more popular than other grades. These pipes can be bare pipes without any coating, or they may be Hot-Dipped or Zinc-Coated and manufactured by Welding or by a Seamless manufacturing process. In Oil and Gas, A53 grade pipes are used in structural and non-critical applications.
ASTM A53 pipe (also referred to as ASME SA53 pipe) is intended for mechanical and pressure applications and is also acceptable for ordinary uses in steam, water, gas, and air lines. It is suitable for welding, and suitable for forming operations involving coiling, bending, and flanging, subject to certain qualifications.
The weld seam is heat treated after welding without untempered martensite remains. Also, the weld flash can be removed from both inner and outer surfaces.
The steel for both seamless and welded pipe shall be made by one or more of the following processes: open-hearth, electric furnace, or basic-oxygen. The weld seam of electric-resistance welded pipe in Grade B shall be heat treated after welding.
Applications: heat exchangers, condensers, heat transfer equipment and similar pipes.
Note:
| Element | Type S | Type E | Type F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (seamless) | (electric-resistance welded) | (furnace-welded pipe) | |||
| Grade A | Grade B | Grade A | Grade B | Grade A | |
| Carbon max. % | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Manganese % | 0.95 | 1.2 | 0.95 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Phosphorous, max. % | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Sulfur, max. % | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Copper, max.% | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Nickel, max. % | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Chromium, max. % | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Molybdenum, max. % | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Vanadium, max. % | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Grade | Rm Mpa Tensile Strength | Mpa Yield Point | Elongation | Delivery Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ≥330 | ≥205 | 20 | Annealed |
| B | ≥415 | ≥240 | 20 | Annealed |
If ordered galvanized, A53 seamless pipe must be coated inside and out via the hot-dip process. Zinc used for galvanized coatings must conform to Specification B6. The weight of this coating must not be less than 1.8 oz./ft2 (0.55 kg/m2). Test specimens for coating weight testing will be cut in approximately 4” lengths.
ASTM A53 B mechanical strength is the same with ASTM A106 B steel pipe, Tensile strength maximum 415 Mpa, Yield strength maximum 240 Mpa.
A53 pipe is best suited for transport of air, water, steam and oil in low- and medium pressure applications across the industrial spectrum. It’s also commonly used as structural steel. A106 pipe is formulated specifically for high-temperature and high-pressure service, usually in power generation applications.
ASTM A53 addresses “Pipe, Steel, Black and Hot-Dipped, Zinc-Coated, Welded and Seamless.” A53 basically covers two different grades of low carbon steel that are hot-dip galvanized in pipe form. The galvanized pipes can be produced in seamless or welded forms.
S355JR is a low carbon steel used for structural applications. It is available in many forms: coils, sheets, pipes, tubes, and heavy structures. It is commonly used in railroads, cranes, dump trucks, offshore structures, and ships. An equivalent ASTM steel specification is ASTM A572 Grade 50.
Short version: ASTM A53 is specific to galvanized pipes made of a low carbon steel. S355JR is a versatile low carbon steel used in many applications.
ASTM A53 specification covers the steel pipe manufacturing types in seamless and welded, material in carbon steel, black steel. Surface natural, black, and hot-dipped galvanized, zinc coated steel pipe. Diameters range from NPS 1?8 to NPS 26 (10.3mm to 660mm), nominal wall thickness.
ASTM A106 standard specification covers the seamless carbon steel pipe, applied for high-temperature services.
Different types and grades for both standard
ASTM A53 steel pipe types and grades
For ASTM A53 there are ERW and seamless steel pipes Type F, E, S covers Grade A and B.
A53 Type F, furnace butt welded, continuous weld Grade A
A53 Type E, Electric resistance welded (ERW), in Grade A and Grade B.
A53 Type S, Seamless steel pipe, in Grade A and Grade B.
If raw steel material of different grades in process of continuously casting, the transition material result shall be identified. And the manufacturer should remove the transition material with the processes that could separate the grades positively.
In case ASTM A53 Grade B in ERW (electric resistance welded) pipe, the weld seam shall be done the heat treatment with a minimum 1000°F [540°C]. In this way the no untempered martensite remains.
In case ASTM A53 B pipe in cold expanded, then expansion should not exceed 1.5% of the required OD.
(Please note the type F is not used for flanging, and if type S or type E is applied for coiling or cold bending, it is recommended to use ASTM A106 Grade A pipe. Although, it is not prohibit to use ASTM A106 Grade B for the cold bending and coiling. According the facility from the manufacturer, type E of ASTM A53 pipe could be supplied non cold expanded or cold expand steel pipe.)
For ASTM A106 steel pipe, manufacturing Type only in seamless, processes hot rolled and the cold drawn. Grade in A, B and C.
ASTM A106 Grade A: Maximum Carbon element 0.25%, Mn 0.27-0.93%. Minimum tensile strength 48000 Psi or 330 Mpa, yield strength 30000 Psi or 205 Mpa.
A106 Grade B: Maximum C below 0.30%, Mn 0.29-1.06%. Minimum tensile strength 60000 Psi or 415 Mpa, yield strength 35000 Psi or 240 Mpa.
Grade C: Maximum C 0.35%, Mn 0.29-1.06%. Minimum tensile strength 70000 Psi or 485 Mpa, yield strength 40000 Psi or 275 Mpa.
As ASTM A106 B is the common use, the chemical here we listed is C≤0.3%, Mn 0.29-1.06%, P≤0.035, S≤0.035%, Si>0.1, Cr≤0.40, Cu≤0.40, Ni≤0.40, Mo≤0.40, V≤0.08.
Differently with ASTM A53 B, ASTM A106 B has Si min 0.1%, which A53 B has 0, so A106 B have better heat resistance than A53 B, since Si improve the heat resistance.
A106 Grade B has low sulfur and phosphorus than A53 B, this is better.
Both pipes applied for mechanical and pressure systems, transporting steam, water, gas, and etc.
ASTM A53 pipe application:
1. Construction, underground transportation, extraction of ground water while building, steam water transportation etc.
2. Bearing sets, machinery parts processing.
3. Electric application: Gas transmission, water power generation fluid pipeline.
4. Wind power plant anti-static tube etc.
5. Pipelines that required zinc coated.
ASTM A106 pipe application:
Especially for high temperature services that up to 750°F, and it could substitute ASTM A53 pipe in most of the cases. In some country at least in United States, usually ASTM A53 is for welded pipe while ASTM A106 is for seamless pipe. And if client asked for ASTM A53 they will also offer A106. In China, manufacturer will offer the pipe that comply to three standards ASTM A53 B / ASTM A106 B / API 5L B.
The production of our seamless pipes is tightly regulated and all of the pipes we stock have been fully tested to international standards to ensure we only supply the highest quality products.
| Product name | Executive standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel code/ Steel grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black and Hot-dipped Zinc-coated Steel Pipes Seamless | ASTM A53 | 0.3-1200 x 1.0-150 | GR.A, GR.B, GR.C |
| Seamless Carbon Steel for High Temperature Service | ASTM A106 | 10.3-1200 x 1.0-150 | GR.B, GR.C |
| Seamless Cold-drawn Low-Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A179 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Carbon Steel Boiler Tubes for High Pressure | ASTM A192 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | Low Carbon Steel |
| Seamless Cold-drawn Intermediate Alloy Steel Heat-exchanger and Condenser Tubes | ASTM A199 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | T5, T22 |
| Seamless Medium-carbon Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes | ASTM A210 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | A1, C |
| Seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy Steel Boiler, Superheater and Heat-exchanger Tubes | ASTM A213 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | T5, T5b, T9 , T11, T22 ,T91 |
| Seamless Carbon and Alloy Steel for Mechanical Tubing | ASTM A333 | 1/4"-42" x SCH20-XXS | Grade1 Gr. 3,Gr..6, Gr.8 , Gr. 9 |
| Seamless Cold-drawn Carbon Steel Feedwater Heater Tubes | ASTM A556 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | A2, B2 |
| Round and shaped steel cold formed welded and seamless carbon steel structural pipe. | ASTM A500 | OD :10.3-820 x 0.8- 75 | Grade A, B, C, D |
| Carbon and alloy steel mechanical tubing, either hot-finished or cold-finished | ASTM A519 | 10.3-426 x 1.0-36 | 1020, 1025, 4130, 4140 |
| For seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe for high-temperature service | ASTM A335 | 1/4"-42" x SCH20-XXS | A/SA 335 P1, P2, P11, P12, P15, P22, P91, P92, P122 |
Cold Drawn Seamless Mechanical Tubing (CDS) is a cold drawn 1018/1026 steel tube which offers uniform tolerances, enhanced machinability and increased strength and tolerances compared to hot-rolled products.

Cold drawn steel tube is with hot-rolled steel coil as raw material, and tandem cold rolling pickled to remove oxide scale, its finished rolling hard roll, rolling hard volumes due to the continuous cold deformation caused by cold hardening strength, hardness increased indicators declined tough plastic, stamping performance will deteriorate, which can only be used for simple deformation of the parts.
Rolling hard roll can be used as the raw material of the hot-dip galvanizing plant, hot dip galvanizing line set annealing line. Rolling hard roll weight is generally 6 to 13.5 tons, the coil diameter of 610mm.
Hot-rolled seamless steel pipe production base deformation process can be summarized as three stages: perforation, extension and finishing.
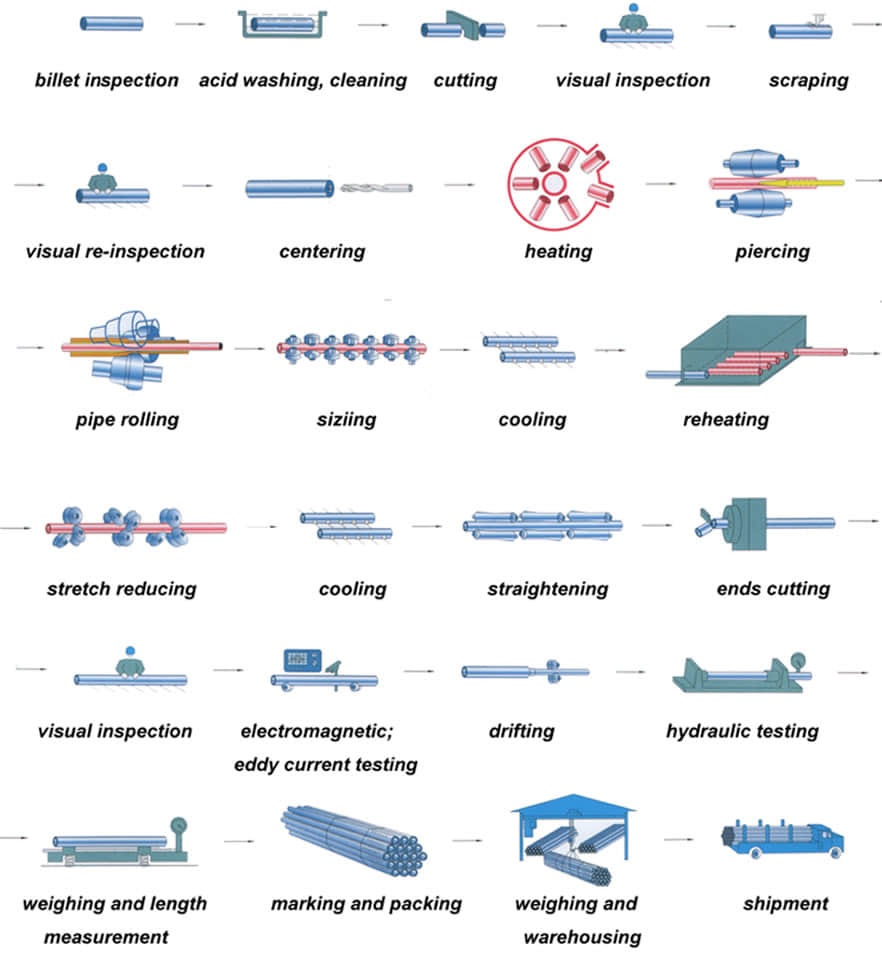
The main purpose of the perforation process is to become a solid round billet piercing hollow shell. Capillary in the specifications, accuracy and surface quality can not meet the requirements of the finished product, further improvements are needed to deform the metal through. The main purpose of the stretching machine is further reduced sectional view (main compression wall) for a larger axial extension, so that the capillary improved dimensional accuracy, surface quality and organizational performance.
After stretching machine rolled steel pipe shortage collectively need further molding mill in order to achieve the requirements of the finished pipe. Rolled steel due to pass in the method widely used in the production of seamless steel tubes.
So far, due to the method pass rolling steel can be divided into two categories: core pension without rolling rolling (hollow body rolling), and with the mandrel. Sizing machines, reducing mill and stretch reducing mill belonging to the hole without mandrel type continuous rolling mills are generally coffin. Its main purpose is to reduce the diameter of the deformation process or sizing get finished steel, the wall thickness of process control, can make thinning, thickening or nearly unchanged.
All the traditional hole-type rolling machine with mandrel belong to extend machine. The main purpose is to reduce the deformation process perforated capillary wall thickness and outer diameter roll passes in the deformation zone and the mandrel posed, for a larger axial extension. At the same time a certain improvement in the organization, performance, accuracy, surface quality.

Before cutting pipe and tubing
No matter the material, measure the diameter of the pipe or tube to be cut to ensure that you use the right-size tube cutter for the job. When determining how to make a straight cut, use a tape measure and a pencil or other writing instrument to mark on the surface where you want to cut. If possible, mark around the circumference of a pipe, especially when cutting with a handsaw. Ensure that a cut is as straight as possible by securing the pipe with a vise, clamp, miter box or even duct tape to keep the length from shifting out of place while cutting.
After cutting pipe and tubing

Geometrical inspection of steel pipes The outer diameter, wall thickness, bending and length of the steel pipe can be inspected on the inspection table with an outer caliper, a micrometer and a bending ruler, and a length tape measure.
Take seamless steel pipe as an example, there are some tolerances that affect quality. Noting this, and you will get a better pipe.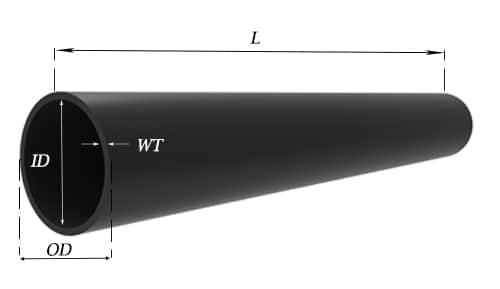
Weight tolerance
For pipe NPS 12 (DN300, 323.8mm) and under, the weight shall vary within -3.5% / +10%.
For pipe over NPS 12 (DN300, 323.8mm), the weight shall vary within -5% / +10%.
Pipe of NPS 4 (DN100, 114.3mm) and smaller may be weighed in convenient lots; pipe in sizes larger than NPS 4 shall be weighed separately.
Quantity tolerance
Normally mills take -10% to +10% tolerance, but TPMCSTEEL keeps ±3% variation.
Length tolerance
For Seamless pipe& tube, if definite cut lengths are ordered, the length shall vary within -0mm / +6mm.
| Pipe types | Pipe Szie(mm) | Tolerances | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot rolled | OD | <50 | ±0.50mm |
| ≥50 | ±1% | ||
| WT | <4 | ±12.5% | |
| ≥4-20 | +15%, -12.5% | ||
| >20 | ±12.5% | ||
| Cold drawn | OD | 6-10 | ±0.20mm |
| 10-30 | ±0.40mm | ||
| 30-50 | ±0.45 | ||
| >50 | ±1% | ||
| WT | <1 | ±0.15mm | |
| >1-3 | + 15%, – 10% | ||
| >3 | + 12.5%, – 10% | ||
| Standard | Hot finished seamless tube | Cold flnished seamless tube | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out diameter (mm) | Tolerance | Out diameter (mm) | Tolerance | |
| EN10216-1 | ≤100 | +/-0.75% (min.+/-0.5mm) | All | +/-0.5% |
| EN10216-2 | (min. +/-0.30mm) | |||
| DIN17175 | >100 | +/-0.90% | ||
| GB/T 3087 | ≤460 | +/-0.75% (min.+/-0.5mm) | 10-30 | +/-0.40mm |
| >30-50 | +/-0.45mm | |||
| >50 | +/-1.0% | |||
| GB/T 5310 GB/T 9948 GB/T 6479 | <57 | +/-0.40mm | ≤30 | +/-0.20mm |
| 57-325 | +/-0.75% | >30-50 | +/-0.30mm | |
| >325-460 | +1%,-2mm | >50 | +/-0.8% | |
| ASME SA-179M ASME SA-192M ASME SA-209M ASME SA-210M ASME SA-213M JIS G 3461 JIS G 3461 | ≤101.6 | +0.4, -0.8mm | <25.4 | +/-0.10mm |
| >25.4-38.1 | +/-0.15mm | |||
| >38.1-50.8 | +/-0.20mm | |||
| 101.6-190.5 | +0.4, -1.2mm | >50.8-63.5 | +/-0.25mm | |
| >63.5-76.2 | +/-0.30mm | |||
| >76.2 | +/-0.38mm | |||
| ASME SA106 ASME SA335 | ≤48.3 | +/-0.40mm | ≤48.3 | +/-0.40mm |
| 48.3-114.3 | +/-0.79mm | |||
| 114.4-219.1 | +1.59, -0.79mm | |||
| 219.2-323.9 | +2.38, -0.79mm | >48.3 | +/-0.79mm | |
| >324 | +/-1.0% | |||
| Standard | Hot finished seamless tube | Cold flnished seamless tube | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIN17175 | Out diameter OD(mm) | Wall thickness T(mm) | Tolerance | Out diameter (mm) | Wall Thickness T(mm) | Tolerance |
| ≤130 | S≤2Sn | +15%, -10% | -- | All | +/-10% (min. +/-0.2mm) |
|
2Sn| +12.5%, -10% |
| |||||
| S>4Sn | +-/9% | |||||
| >130 | S≤0.05da | +17.5%, -12.5% | ||||
0.05da| +/-12.5% |
| |||||
| S>0.11da | +/-10% | |||||
| EN 10216-1 EN 10216-2 | ≤219.1 | - | +/-12.5% (min.+/-0.4mm) |
|||
| -- | T/D≤0.025 | +/-20% | ||||
0.025| +/-15% |
| |||||
0.05| +/-12.5% |
| |||||
0.1| +/-10% |
| |||||
| GB/T 3087 | -- | ≤20 | +15%,-12.5% (min.+0.45, -0.35mm) | -- | 1.0-3.0 | +15%, -10% |
| >20 | +/-12.5% | -- | >3 | +12.5%, -10% | ||
| GB/T 5310 GB/T 9948 GB/T 6479 | -- | <4.0 | +15%,-10% (min.+0.48, -0.32mm) | -- | 2-3 | +12%,-10% |
| 4-20 | +12.5%,-10% | >3 | +/-10% | |||
| >20 | +/-10% | |||||
| ASME SA-179M ASME SA-192M ASME SA-209M ASME SA-210M ASME SA-231M JIS G 3461 JIS G 3462 | -- | 2.41-3.8 | +35%, -0% | ≤38.1 | -- | +20%,-0% |
| 3.8-4.6 | +33%,-0% | >38.1 | -- | 22%,-0% | ||
| >4.6 | +28%,-0% | -- | -- | -- | ||
| ASME SA-106 ASME SA-335 | -- | All | +/12.5% | All | +/-10% | |
Note:

Positive material identification (PMI) testing is the examination of a material, usually a metallic alloy, to confirm the material is consistent with the user’s request.
Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
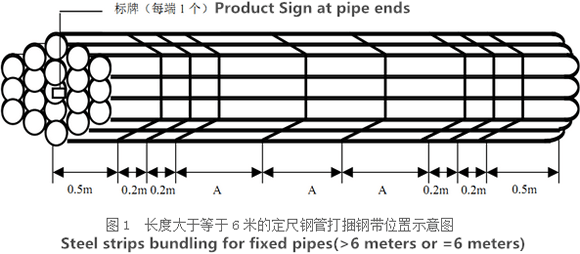
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment.
Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free?
A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment
Q: What is the packaging and transportation form?
A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity?
A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.