Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

Alloy steel U tubes are the fluid inlet and outlet were installed in the same side on both sides of the head with partitions into two rooms, each tube is free to expand and retract to solve the heat Compensation problem.
Alloy steel U tubes are the fluid inlet and outlet were installed in the same side on both sides of the head with partitions into two rooms, each tube is free to expand and retract to solve the heat Compensation problem.
U bend tubes for heat exchangers applied mostly in oil and gas plants, chemical and petrochemical plants, refineries, power plants and renewable energy plants. Low fin tubes can be supplied in the form of U bends.
U-bend tubes are widely used in heat-exchanger systems. Heat-exchanger equipment on the basis of seamless stainless U-tubes is essential in strategically important and critical fields — nuclear and petrochemical machine building.

| Item | Condition (when) | Tolercance |
|---|---|---|
| Ovality | Nominal bend radius ≤ 2 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 12% |
| 2 x nominal OD < Nominal bend radius ≤ 4 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 10% | |
| Nominal bend radius > 4 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 5% | |
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 2 x nominal OD | 0.75 x nominal wall | |
| Mimimum wall thickness | 2 x nominal OD < Nominal bend radius ≤ 4 x nominal OD | 0.8 x nominal wall |
| Nominal bend radius > 4 x nominal OD | 0.9 x nominal wall | |
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 8″ (200mm) | +/-3/64″(1mm) | |
| Bending Radius | 8″ (200mm) < Nominal bend radius ≤ 16″ (400mm) | +/-1/16″(1mm) |
| Nominal bend radius >16″ (400mm) | +/-5/64″(1mm) | |
| Disrance between legs | Max 1/16″(1.5mm) | |
| Wall thinning of bending area | Max 17% | |
| Difference between leg lengths at the ends | Leg length ≤ 16′ (4.88m) | +1/8″(3mm) |
| Leg length > 16′ (4.88m) | +3/16″(5mm) | |
| Deviation from plane of bend | ≤ 3/16″(1.5mm) | |
| Flattening on bend | ≤ 10% nominal diameter | |
| Straight leg length | ≤5m | +1/8″(3mm) |
| >5m | +3/16(5mm) | |
| Total tube length including radius | ≤6m | +3/16(5mm) |
| >6m | +5/16″(8mm) |
Alloy Steel U-tube heat exchanger tubes are bent into a U-shaped tube, the fluid inlet and outlet were installed in the same side on both sides of the head with partitions into two rooms, each tube is free to expand and retract to solve the heat Compensation problem.
The U tube is an important part of the U tube heat exchanger.
The main structure of the U type tube heat exchanger includes the tube box, the barrel, the head, the heat exchange tube, the nozzle, the baffle plate, the punching plate and the guide tube, the short circuit structure, the support and other accessories.
Alloy Steel U tubes used for heat transfer tubes is usually used for heat transfer tubes and ordinary cold drawn tubes. The former is suitable for non phase transition heat transfer and vibration prone situations, and the latter is suitable for reboiling, condensing heat transfer and non vibration general situations.
Alloy Steel U tubes has a variety of forms, smooth tube is the most traditional form, because it has the advantages of easy manufacturing and low unit length cost, which is the most common in the current application. The pipe should be able to withstand certain temperature and stress. When the tube and shell side fluid are corrosive, the pipe should also have corrosion resistance.
The material of Alloy Steel U tubes:T5, T11, T12, T22, T9, T91, etc.
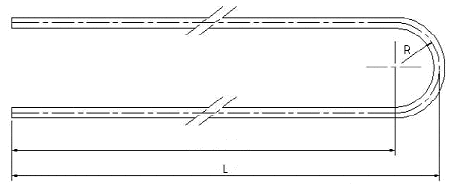 The semi-finished product for U bend tubes are heat exchanger tubes, manufactured and supplied according to DIN 28180 and ASTM A179. Tubes for heat exchangers are made of steel according to:
The semi-finished product for U bend tubes are heat exchanger tubes, manufactured and supplied according to DIN 28180 and ASTM A179. Tubes for heat exchangers are made of steel according to:
other types of steel can be supplied by agreement.
U bend tubes for heat exchangers applied mostly in oil and gas plants, chemical and petrochemical plants, refineries, power plants and renewable energy plants. Low fin tubes can be supplied in the form of u bends.
Post bending heat treatment by electrical resistance (Joule effect) is applied. The temperature is monitored and controlled during the process. It is possible to perform the heat treatment in a nitrogen atmosphere.
Heat Treatment Equipment
Sizes tolerances of U bend tubes are to fulfil the requirements of: ASTM A556 / 556M and DIN 28 179

‘U’ bends are produced, controlled and measured fully in accordance with relevant standards.
Material / Grade
 Here is a list for providing ovality, minimum wall thickness, bending radius, distance between legs, wall thinning of bending area and so on. Thus, we can figure out which kind of type would be our final choice for our engineering project.
Here is a list for providing ovality, minimum wall thickness, bending radius, distance between legs, wall thinning of bending area and so on. Thus, we can figure out which kind of type would be our final choice for our engineering project.
| Item | Condition (when) | Tolercance |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 2 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 12% | |
| Ovality | 2 x nominal OD < Nominal bend radius ≤ 4 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 10% |
| Nominal bend radius > 4 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 5% | |
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 2 x nominal OD | 0.75 x nominal wall | |
| Mimimum wall thickness | 2 x nominal OD < Nominal bend radius ≤ 4 x nominal OD | 0.8 x nominal wall |
| Nominal bend radius > 4 x nominal OD | 0.9 x nominal wall | |
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 8" (200mm) | +/-3/64"(1mm) | |
| Bending Radius | 8" (200mm) < Nominal bend radius ≤ 16" (400mm) | +/-1/16"(1mm) |
| Nominal bend radius >16" (400mm) | +/-5/64"(1mm) | |
| Disrance between legs | Max 1/16"(1.5mm) | |
| Wall thinning of bending area | Max 17% | |
| Difference between leg lengths at the ends | Leg length ≤ 16' (4.88m) | +1/8"(3mm) |
| Leg length > 16' (4.88m) | +3/16"(5mm) | |
| Deviation from plane of bend | ≤ 3/16"(1.5mm) | |
| Flattening on bend | ≤ 10% nominal diameter | |
| Straight leg length | ≤5m | +1/8"(3mm) |
| >5m | +3/16(5mm) | |
| Total tube length including radius | ≤6m | +3/16(5mm) |
| >6m | +5/16"(8mm) |
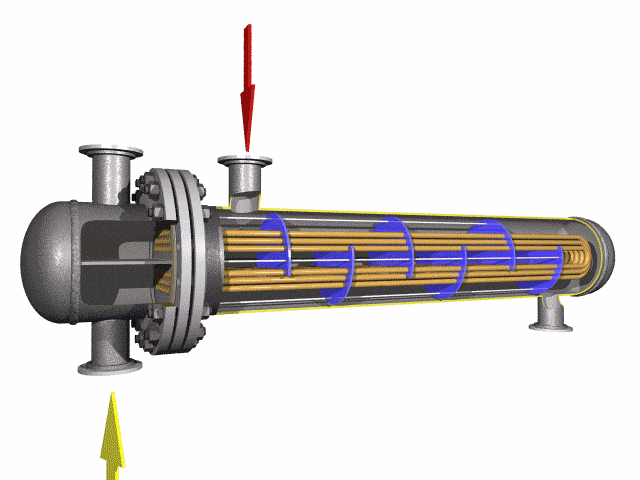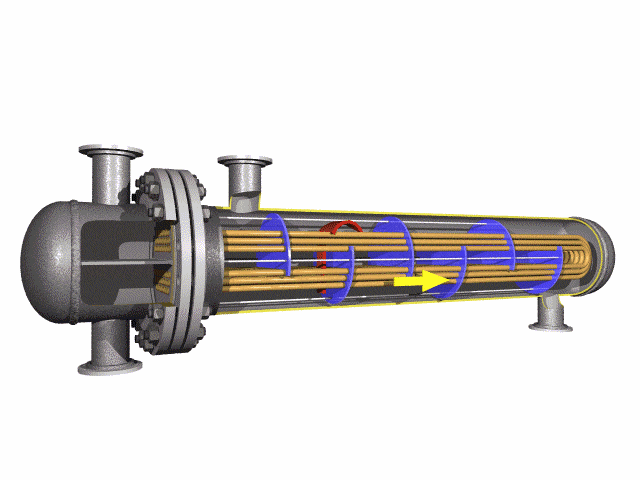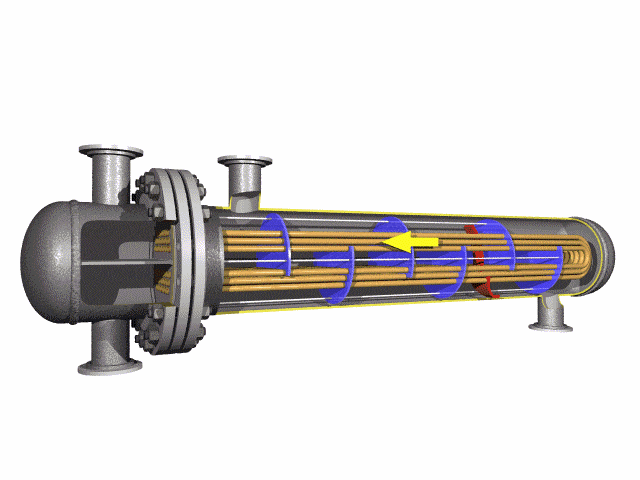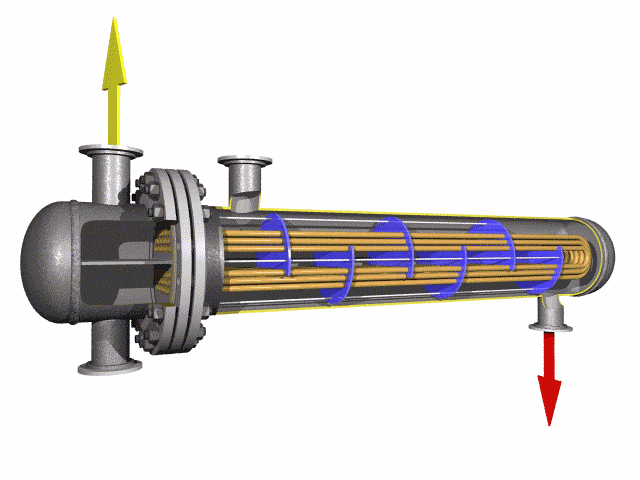
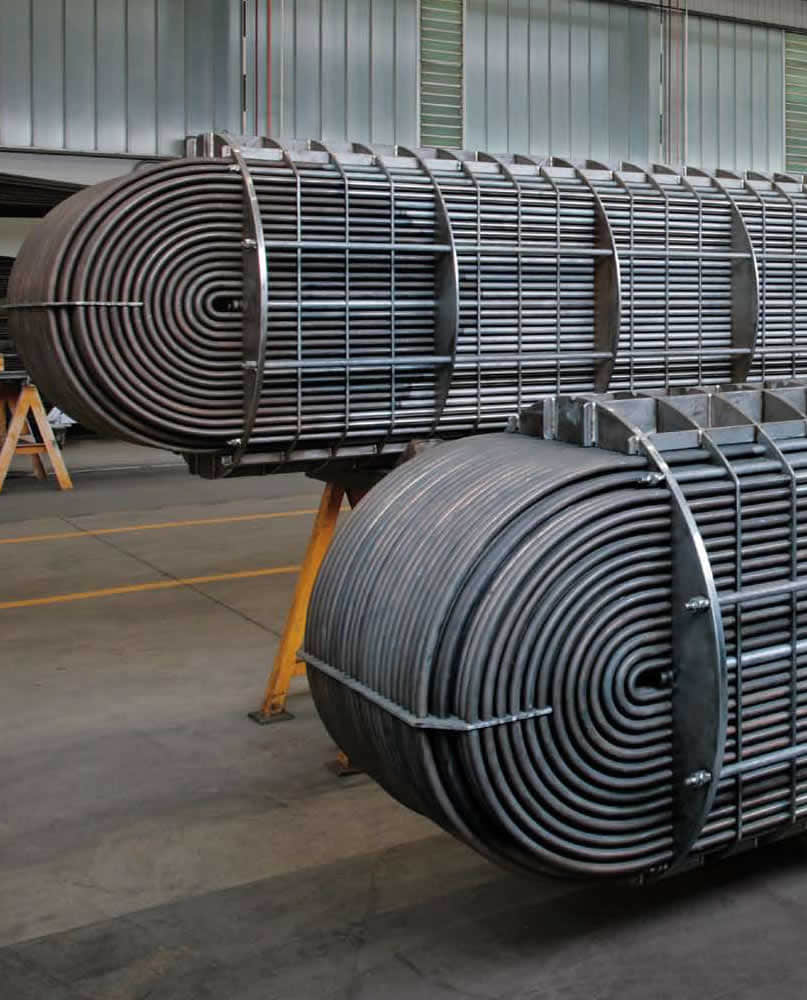
U-bend tubes are widely used in heat-exchanger systems.
Heat-exchanger equipment on the basis of seamless stainless U-tubes is essential in strategically important and critical fields — nuclear and petrochemical machine building.

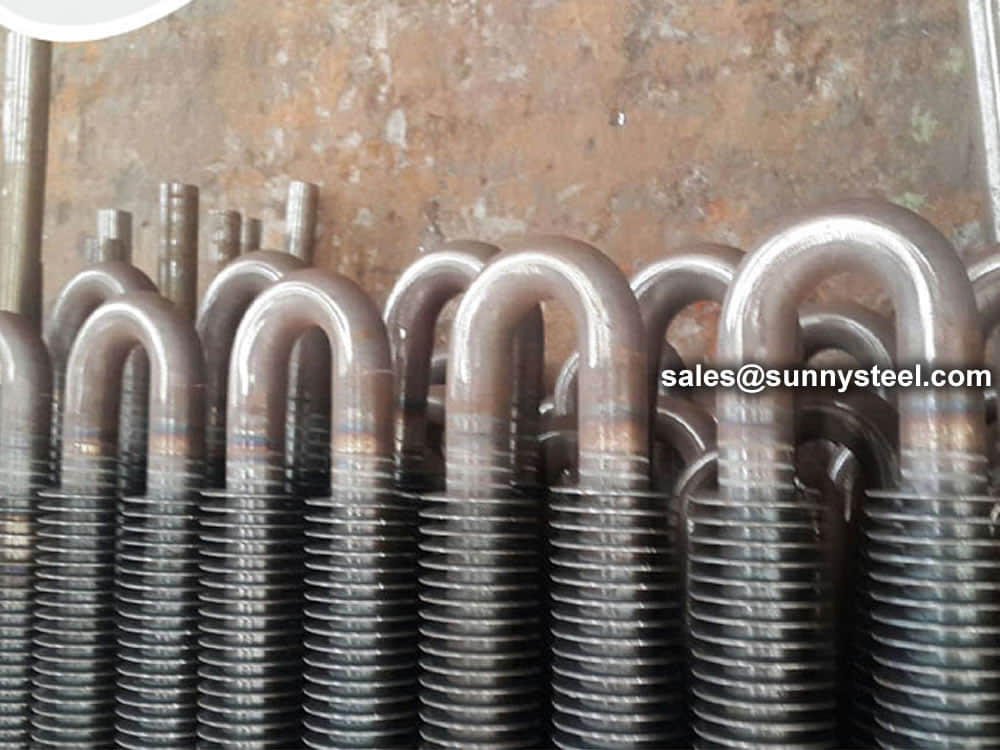
U tube heat exchanger is characterized by its simple structure, good tightness, convenient maintenance and cleaning, low cost, good thermal compensation performance and strong pressure bearing capacity. The U-tube heat exchanger has the largest heat exchange area under the same diameter. The main structure of U-shaped tube heat exchanger includes tube box, cylinder, head, heat exchange tube, nozzles, baffle, anti-shock plate and guide tube, anti-short circuit structure, support and other accessories of the shell and tube side, is the most commonly used in shell and tube heat exchanger.
Tube sheet
Tube sheet is one of the most important parts of shell – tube heat exchanger. The tube plate is the barrier between the shell side and the pipe side. When the heat exchange medium has no corrosion or slight corrosion, it is generally made of low carbon steel, low alloy steel or stainless steel. The connection form of tube-sheet and shell is divided into non-detachable and detachable types. The former is the connection between tube-sheet and shell in the fixed tube-sheet heat exchanger. The latter, such as U-shaped tube type, floating head type and stuffing box type and sliding tube plate type heat exchanger tube plate and shell connection. For removable connections, the tube plate itself is usually not in direct contact with the shell, but the flange is connected to the shell indirectly or is clamped by two flanges on the shell and the tube box.
Tube box
Most of the shell tube heat exchangers with larger shell diameters adopt tube and box structures. The tube box is located at both ends of the heat exchanger, which evenly distributes the fluid from the pipe to the heat exchanger tubes and gathers the fluid in the tubes together to send out the heat exchanger. In a multi-pipe shell, the casing can also change the flow direction. The structure of the tube box is mainly determined by whether the heat exchanger needs to be cleaned or whether the tube bundle needs to be divided.
Perhaps the best known use of tube sheets are as supporting elements in heat exchangers and boilers. These devices consist of a dense arrangement of thin walled tubes situated inside an enclosed, tubular shell. Tubes are supported on either end by sheets which are drilled in a predetermined pattern to allow the tube ends to pass through the sheet. The ends of the tubes which penetrate the tube sheet are expanded to lock them in place and form a seal. The tube hole pattern or “pitch” varies the distance from one tube to the other and angle of the tubes relative to each other and to the direction of flow. This allows the manipulation of fluid velocities and pressure drop, and provides the maximum amount of turbulence and tube surface contact for effective Heat Transfer.
In cases where it is critical to avoid fluid intermixing, a double tube sheet can be provided. The design of tube sheets is a fairly precise and complex process; the exact number of tubes needs to be established and a pattern of holes calculated to spreads them evenly over the tube sheet surface. Large exchangers may have several thousand tubes running through them arranged into precisely calculated groups or bundles. Sheet design and production is largely automated these days with computer software (like CAD) performing the calculations and the tube sheet drilling done on computer numerical control (CNC) machines. In this design, the outer tube sheet is outside the shell circuit, virtually eliminating the chance of fluid intermixing. The inner tube sheet is vented to atmosphere so any fluid leak is easily detected. Duwa Piping factory drilling department has professional drilling equipment and working team, we can provide the best quality tube sheet for you.

Fin tubes are used in applications involving the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a colder fluid through a tube wall. Furthermore, finned tubes are used when the heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the tubes is appreciably lower than that on the inside.
Before their shipment, we will conduct a comprehensive inspection. The inspection contains: size, thickness, length, radius and marking.
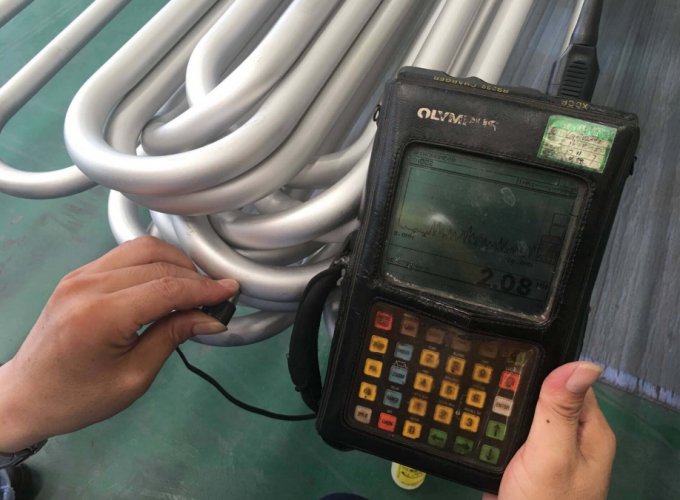

Size inspection

PMI test
Any type of packing U bend tubes is available according to customer need to worldwide destinations.
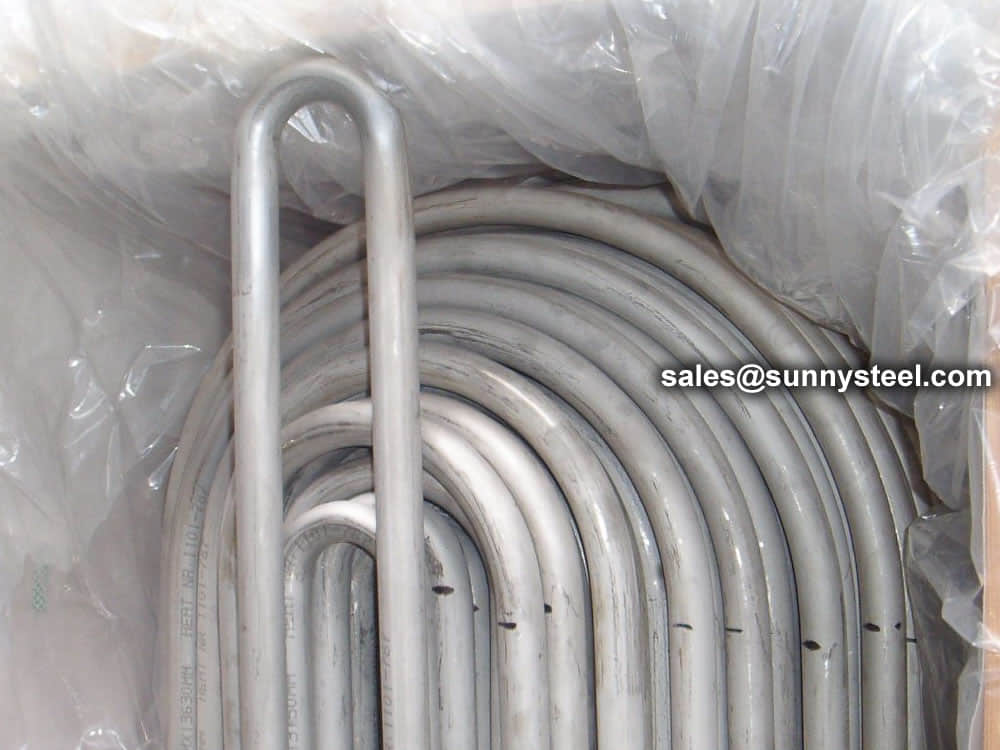

Stainless steel U bend tubes
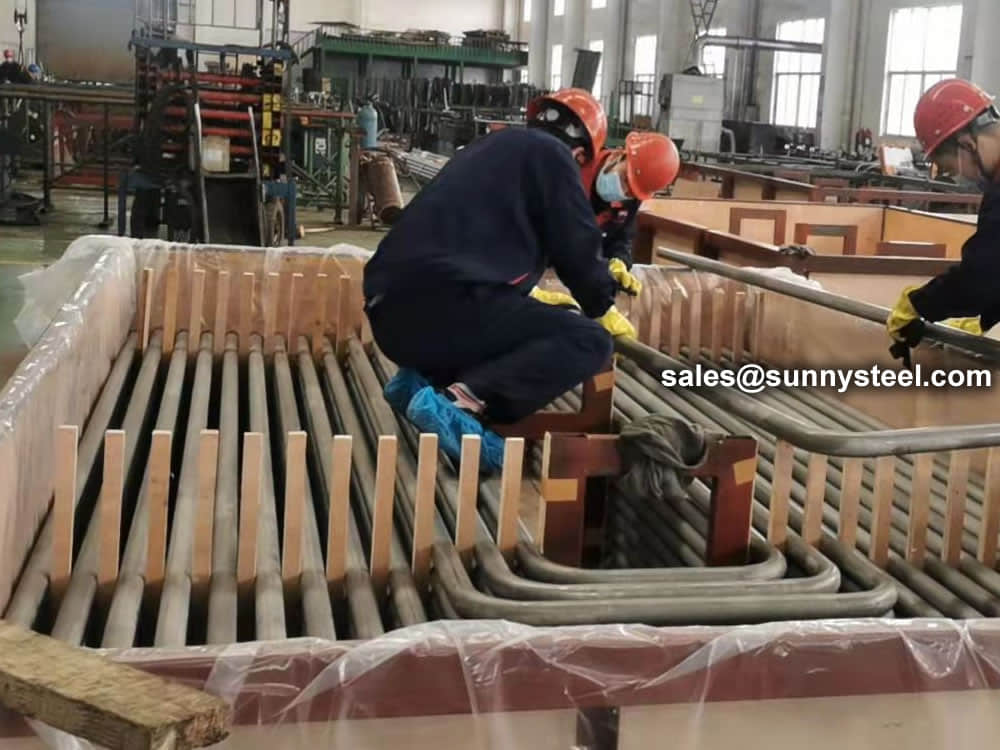

SA 213 TP347H stainless tubes
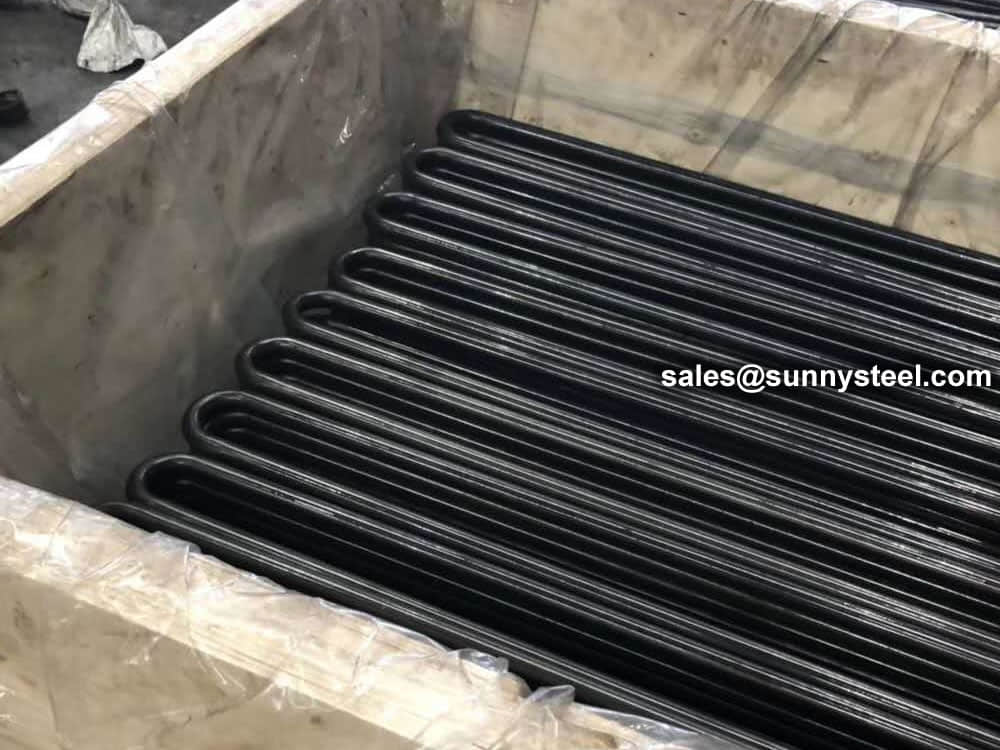

ASTM A179 U bend tubes
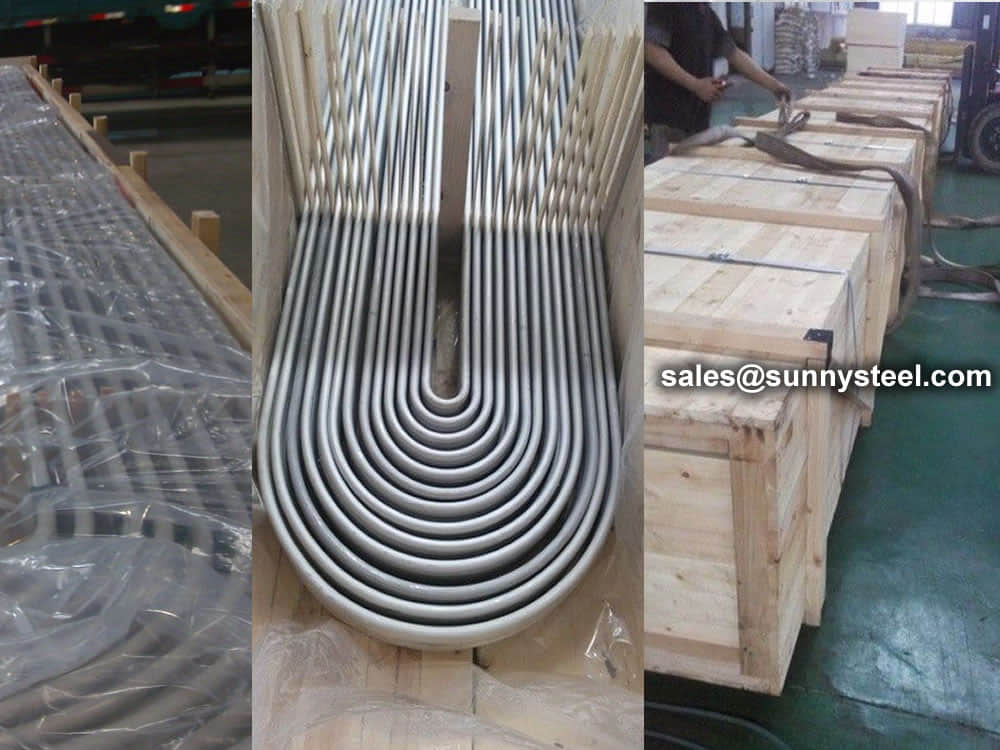

U bend tubes are packed in wooden cases
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment.
Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free?
A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee.
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment
Q: What is the packaging and transportation form?
A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea.
Q: What is your minimum order quantity?
A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.