Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

A234 WPB Large Diameter Pipe Cap are used for connecting pipes of different diameters and find wide applications in various chemicals, construction industries, paper, cement & ship builders. We offer all SA234 WPB Pipe Caps at really low prices with prompt and efficient delivery. Our Carbon Steel ASTM A234 WPB Cap range can meet all your size and grade requirements & ready for immediate despatch. These onsite facilities for CS A234 WPB Cap enable us to offer a large range of testing to suit exact customer requirements and to export all Cap ASTM A234 WPB with 100% weld radiography, without impacting on our short lead-times.
A234 WPB Large Diameter Pipe Cap are used for connecting pipes of different diameters and find wide applications in various chemicals, construction industries, paper, cement & ship builders. We offer all SA234 WPB Pipe Caps at really low prices with prompt and efficient delivery. Our Carbon Steel ASTM A234 WPB Cap range can meet all your size and grade requirements & ready for immediate despatch. These onsite facilities for CS A234 WPB Cap enable us to offer a large range of testing to suit exact customer requirements and to export all Cap ASTM A234 WPB with 100% weld radiography, without impacting on our short lead-times.
The pipe end cap helps protect the end of the pipes of various shapes, and its main purpose is to make the connections waterproof. The ASTM A234 WPB Pipe End Cap can be used to close the ends of hydraulic or pneumatic pipes and tubes. The ASTM A234 WPB Cap is mostly made of carbon steel with a minimum yield strength of 240MPa and minimum tensile strength of 585MPa, which helps the pipe fit to work in a high stress environment. We are one of the top manufacturers of A234 WPB Pipe Cap where A234 WPB is the standard determination for fittings of fashioned carbon steel and alloy steel for direct and high-temperature services. In addition, we have a vast stock of SA 234 Gr WPB SCH 80 Caps which can find its application in various industries.
| Grade | Type | C | Si | S | P | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Other | ób | ós | δ5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPB | 0.3 | 0.1min | 0.058 | 0.05 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | V:0.06;Nb:0.02 | 415-585 | 240 | 22 | 197 |
| WPC | 0.35 | 0.1min | 0.058 | 0.05 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | V:0.06;Nb:0.02 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 |
| WP1 | 0.28 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.9 | 0.44-0.65 | 380-550 | 205 | 22 | 197 | |||
| WP12 CL1 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.6 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 220 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP12 CL2 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.6 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL1 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5-1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL2 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.8 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL3 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.8 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP22 CL1 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP22 CL3 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP5 CL1 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 4-6 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP5 CL3 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 4-6 | 0.44-0.65 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP9 CL1 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-10 | 0.9-1.1 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP9 CL3 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-10 | 0.9-1.1 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WPR | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.045 | 0.4-1.06 | 1.6-2.24 | 435-605 | 315 | 22/28 | 217 | ||||
| WP91 | 0.08-0.12 | 0.2-0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-9.5 | 0.4 | 0.85-1.05 | See sdandard | 585-760 | 415 | 20 | 248 |
| WP911 | 0.09-0.13 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 8.5-10.5 | 0.4 | 0.9-1.1 | See sdandard | 620-840 | 440 | 20 | 248 |
| Tensile Requirements | WPB | WPC, WP11CL2 | WP11CL1 | WP11CL3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min, ksi[MPa] (0.2% offset or 0.5% extension-under-load) | 60-85 [415-585] | 70-95 [485-655] | 60-85 [415-585] | 75-100 [520-690] |
| Yield Strength, min, ksi[MPa] | 32 [240] | 40 [275] | 30 [205] | 45 [310] |
| OD | ND | INCH | SCH20 | SCH40 | SCH80 | STD | XS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Weight | Weight | Weight | Weight | |||
| 88.9 | 80 | 3 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.92 | |
| 114.3 | 100 | 4 | 1.17 | 1.67 | 1.17 | 1.67 | |
| 141.3 | 125 | 5 | 1.91 | 2.78 | 1.91 | 2.78 | |
| 168.3 | 150 | 6 | 2.9 | 4.47 | 2.9 | 4.47 | |
| 219.1 | 200 | 8 | 4.09 | 5.19 | 8.05 | 5.19 | 8.05 |
| 273 | 250 | 10 | 6.36 | 9.15 | 12.5 | 9.15 | 12.5 |
| 323.8 | 300 | 12 | 9.08 | 14.4 | 26.8 | 13.2 | 17.3 |
| 355.6 | 350 | 14 | 13.2 | 18.8 | 34.5 | 15.9 | 20.4 |
| 406.4 | 400 | 16 | 16.8 | 26.7 | 47.7 | 20.4 | 26.3 |
| 457.2 | 450 | 18 | 24.8 | 41.8 | 67.7 | 25.9 | 33.6 |
| 508 | 500 | 20 | 32.2 | 54.9 | 91.3 | 32.2 | 42.7 |
| 558.8 | 550 | 22 | 37.7 | 49.9 | |||
| 609.6 | 600 | 24 | 46.3 | 93.1 | 155 | 46.3 | 59.5 |
Carbon steel caps manufactured using superior grade raw materials. Carbon steel caps are used for connecting pipes of different diameters and find wide applications in various chemicals, construction industries, paper, cement & ship builders.
| Nominal | Outside Diameter | 90° Elbows | 45° Elbows | 180° Returns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size | Long Radius | Short Radius | Long Radius | Long Radius | ||||
| (inches) | (mm) | (inches) | Center to Face | Center to Face | Center to Face | Radius | Center to Center | Back to face |
| (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | |||
| 1/2 | 21.3 | 0.84 | 1.5 | – | 5/8 | 2 | 1.875 | |
| 3/4 | 26.7 | 1.05 | 1.125 | – | 7/16 | 2.25 | 1.6875 | |
| 1 | 33.4 | 1.315 | 1.5 | 1 | 7/8 | 3 | 2.1875 | |
| 1.25 | 42.2 | 1.66 | 1.875 | 1.25 | 1 | 3.75 | 2.75 | |
| 1.5 | 48.3 | 1.9 | 2.25 | 1.5 | 1.125 | 3 | 4.5 | 3.25 |
| 2 | 60.3 | 2.375 | 3 | 2 | 1.375 | 4 | 6 | 4.1875 |
| 2.5 | 73 | 2.875 | 3.75 | 2.5 | 1.75 | 5 | 7.5 | 5.1875 |
| 3 | 88.9 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 3.5 | 101.6 | 4 | 5.25 | 3.5 | 2.25 | 7 | 10.5 | 7.25 |
| 4 | 114.3 | 4.5 | 6 | 4 | 2.5 | 8 | 12 | 8.25 |
| 5 | 141.3 | 5.563 | 7.5 | 5 | 3.125 | 10 | 15 | 10.3125 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 6.625 | 9 | 6 | 3.75 | 12 | 18 | 12.3125 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 8.625 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 12 | 24 | 16.3125 |
| 10 | 273.1 | 10.75 | 15 | 10 | 6.25 | 15 | 30 | 20.375 |
| 12 | 323.9 | 12.75 | 18 | 12 | 7.5 | 18 | 36 | 24.375 |
Pipe caps are widely well-known for the utmost output and outstanding results that it gives.
Surface treatment:
Pipe caps can be in various shapes.
Reasonable price with excellent quality
Abundant stock and prompt delivery
Rich supply and export experience, sincere service
Reliable forwarder, 2-hour away from port.
Bending, squeezing, pressing, forging, machining and more
Pipe Caps are used for connecting pipes of different diameters and find wide applications in various chemicals, construction industries, paper, cement & ship builders.
 Lifting and handling of a Pressure vessel
Lifting and handling of a Pressure vessel
Pipe caps are widely well-known for the utmost output and outstanding results that it gives.
Size range:
Out diameter: 1/2″-60″ DN15-DN1500
Wall Thickness: sch10-80s
Pressure: SCH5 to SCH160v
Max. wall thickness: 200mm
Bending, squeezing, pressing, forging, machining and more
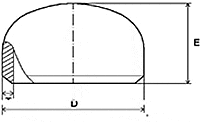 Sunny Steel are Manufacturer, Exporter and Supplier of Pipe Cap. Pipe caps are widely well-known for the utmost output and outstanding results that it gives. Pipe Cap manufactured using superior grade raw materials.
Sunny Steel are Manufacturer, Exporter and Supplier of Pipe Cap. Pipe caps are widely well-known for the utmost output and outstanding results that it gives. Pipe Cap manufactured using superior grade raw materials.
Pipe Cap are used for connecting pipes of different diameters and find wide applications in various chemicals, construction industries, paper, cement & ship builders
| Out diameter | High size | Wall thickness accord to 'E' | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN | NPS | E | E1 | E |
| 15 | 1/2 | 25 | 25 | 3.73 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 25 | 25 | 3.91 |
| 25 | 1 | 38 | 38 | 4.55 |
| 32 | 1 1/4 | 38 | 38 | 4.85 |
| 40 | 1 1/2 | 38 | 38 | 5.08 |
| 50 | 2 | 38 | 44 | 5.54 |
| 65 | 2 1/2 | 38 | 51 | 7.01 |
| 80 | 3 | 51 | 64 | 7.62 |
| 90 | 3 1/2 | 64 | 76 | 8.08 |
| 100 | 4 | 64 | 76 | 8.56 |
| 125 | 5 | 76 | 89 | 9.53 |
| 150 | 6 | 89 | 102 | 10.97 |
| 200 | 8 | 102 | 127 | 12.7 |
| 250 | 10 | 127 | 152 | 12.7 |
| 300 | 12 | 152 | 178 | 12.7 |
| 350 | 14 | 165 | 191 | 12.7 |
| 400 | 16 | 178 | 203 | 12.7 |
| 450 | 18 | 203 | 229 | 12.7 |
| 500 | 20 | 229 | 254 | 12.7 |
| 550 | 22 | 254 | 254 | 12.7 |
| 600 | 24 | 267 | 305 | 12.7 |
| 650 | 26 | 267 | ||
| 700 | 28 | 267 | ||
| 750 | 30 | 267 | ||
| 800 | 32 | 267 | ||
| 850 | 34 | 267 | ||
| 900 | 36 | 267 | ||
| 950 | 38 | 305 | ||
| 1000 | 40 | 305 | ||
| 1050 | 42 | 305 | ||
| 1100 | 44 | 343 | ||
| 1150 | 46 | 343 | ||
| 1200 | 48 | 343 | ||
| OD | ND | INCH | SCH20 | SCH40 | SCH80 | STD | XS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Weight | Weight | Weight | Weight | |||
| 88.9 | 80 | 3 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.92 | |
| 114.3 | 100 | 4 | 1.17 | 1.67 | 1.17 | 1.67 | |
| 141.3 | 125 | 5 | 1.91 | 2.78 | 1.91 | 2.78 | |
| 168.3 | 150 | 6 | 2.9 | 4.47 | 2.9 | 4.47 | |
| 219.1 | 200 | 8 | 4.09 | 5.19 | 8.05 | 5.19 | 8.05 |
| 273 | 250 | 10 | 6.36 | 9.15 | 12.5 | 9.15 | 12.5 |
| 323.8 | 300 | 12 | 9.08 | 14.4 | 26.8 | 13.2 | 17.3 |
| 355.6 | 350 | 14 | 13.2 | 18.8 | 34.5 | 15.9 | 20.4 |
| 406.4 | 400 | 16 | 16.8 | 26.7 | 47.7 | 20.4 | 26.3 |
| 457.2 | 450 | 18 | 24.8 | 41.8 | 67.7 | 25.9 | 33.6 |
| 508 | 500 | 20 | 32.2 | 54.9 | 91.3 | 32.2 | 42.7 |
| 558.8 | 550 | 22 | 37.7 | 49.9 | |||
| 609.6 | 600 | 24 | 46.3 | 93.1 | 155 | 46.3 | 59.5 |
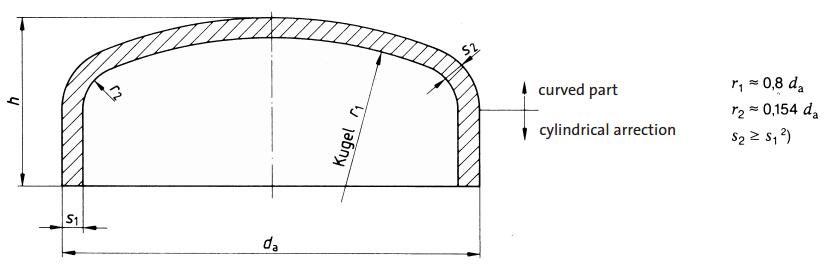
| Outside diameter | Wall thickness | Height | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| mm | mm | mm | kg |
| D | s1 | ||
| 21,3 | 2,0 | 25,0 | 0,060 |
| 26,9 | 2,3 | 32,0 | 0,070 |
| 33,7 | 2,6 | 38,0 | 0,110 |
| 3,2 | 0,130 | ||
| 42,4 | 2,6 | 38,0 | 0,130 |
| 3,6 | 0,170 | ||
| 48,3 | 2,6 | 38,0 | 0,200 |
| 4,0 | 0,230 | ||
| 60,3 | 2,9 | 38,0 | 0,280 |
| 4,5 | 0,320 | ||
| 76,1 | 2,9 | 38,0 | 0,340 |
| 5,0 | 0,390 | ||
| 88,9 | 3,2 | 51,0 | 0,530 |
| 5,6 | 0,700 | ||
| 108,0 | 3,6 | 64,0 | 1,000 |
| 114,3 | 3,6 | 64,0 | 1,000 |
| 6,3 | 1,500 | ||
| 133,0 | 4,0 | 76,0 | 1,600 |
| 139,7 | 4,0 | 76,0 | 1,700 |
| 6,3 | 2,500 | ||
| 159,0 | 4,5 | 90,0 | 2,400 |
| 168,3 | 4,5 | 89,0 | 2,650 |
| 7,1 | 3,550 | ||
| 219,0 | 6,3 | 100,0 | 5,550 |
| 8,0 | 6,700 | ||
| 273,0 | 6,3 | 127,0 | 8,800 |
| 323,9 | 7,1 | 152,0 | 14,000 |
| 355,6 | 8,0 | 165,0 | 16,500 |
| 406,4 | 8,8 | 178,0 | 18,200 |
| 508,0 | 11,0 | 229,0 | 38,000 |
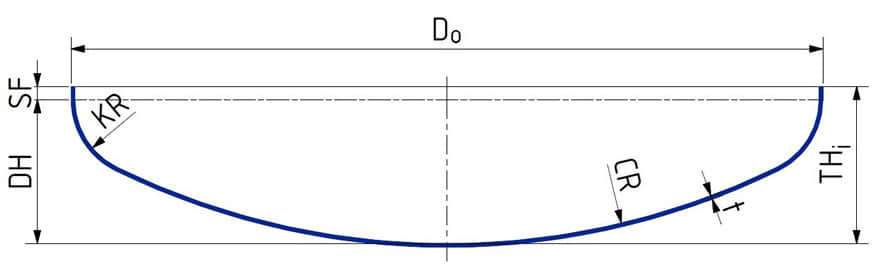
| dimensions d1 x s | height L | weight / kg |
|---|---|---|
| 21,3 x 2,0 | 9,0 | 0,01 |
| 26,9 x 2,0 | 9,0 | 0,01 |
| 33,7 x 2,0 | 13,0 | 0,02 |
| 42,4 x 2,0 | 13,0 | 0,04 |
| 48,3 x 2,0 | 13,5 | 0,05 |
| 60,3 x 2,0 | 18,5 | 0,07 |
| 76,1 x 2,0 | 20,5 | 0,10 |
| 88,9 x 2,0 | 25,0 | 0,15 |
| 114,3 x 2,0 | 28,0 | 0,26 |
| 114,3 x 3,0 | 29,0 | 0,39 |
| 139,7 x 3,0 | 38,5 | 0,60 |
| 168,3 x 3,0 | 47,5 | 0,90 |
| 219,1 x 3,0 | 63,5 | 1,32 |
| 273,0 x 3,0 | 93,0 | 1,95 |
| 323,9 x 3,0 | 102,0 | 2,70 |
| 355,6 x 3,0 | 109,0 | 3,80 |
| 406,4 x 3,0 | 123,0 | 5,00 |
| 457,2 x 3,0 | 123,0 | 6,10 |
| 508,0 x 3,0 | 133,0 | 7,60 |
| dimensions d1 x s | height L | weight / kg |
|---|---|---|
| 20,0 x 2,0 | 9,0 | 0,02 |
| 25,0 x 2,0 | 9,0 | 0,03 |
| 30,0 x 2,0 | 13,5 | 0,03 |
| 35,0 x 2,0 | 13,5 | 0,04 |
| 44,0 x 2,0 | 15,0 | 0,04 |
| 54,0 x 2,0 | 15,0 | 0,05 |
| 70,0 x 2,0 | 19,5 | 0,07 |
| 84,0 x 2,0 | 24,0 | 0,15 |
| 104,0 x 2,0 | 28,0 | 0,20 |
| 129,0 x 2,0 | 37,0 | 0,36 |
| 154,0 x 2,0 | 43,0 | 0,50 |
| 156,0 x 3,0 | 44,0 | 0,94 |
| 204,0 x 2,0 | 62,0 | 0,80 |
| 206,0 x 3,0 | 63,0 | 1,20 |
| 254,0 x 2,0 | 72,0 | 1,30 |
| 256,0 x 3,0 | 73,0 | 1,95 |
| 306,0 x 3,0 | 83,0 | 2,50 |
| Out diameter | High size | Wall thickness accord to 'E' | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN | NPS | E | E1 | E |
| 15 | 1/2 | 25 | 25 | 3.73 |
| 20 | 3/4 | 25 | 25 | 3.91 |
| 25 | 1 | 38 | 38 | 4.55 |
| 32 | 1 1/4 | 38 | 38 | 4.85 |
| 40 | 1 1/2 | 38 | 38 | 5.08 |
| 50 | 2 | 38 | 44 | 5.54 |
| 65 | 2 1/2 | 38 | 51 | 7.01 |
| 80 | 3 | 51 | 64 | 7.62 |
| 90 | 3 1/2 | 64 | 76 | 8.08 |
| 100 | 4 | 64 | 76 | 8.56 |
| 125 | 5 | 76 | 89 | 9.53 |
| 150 | 6 | 89 | 102 | 10.97 |
| 200 | 8 | 102 | 127 | 12.7 |
| 250 | 10 | 127 | 152 | 12.7 |
| 300 | 12 | 152 | 178 | 12.7 |
| 350 | 14 | 165 | 191 | 12.7 |
| 400 | 16 | 178 | 203 | 12.7 |
| 450 | 18 | 203 | 229 | 12.7 |
| 500 | 20 | 229 | 254 | 12.7 |
| 550 | 22 | 254 | 254 | 12.7 |
| 600 | 24 | 267 | 305 | 12.7 |
| 650 | 26 | 267 | ||
| 700 | 28 | 267 | ||
| 750 | 30 | 267 | ||
| 800 | 32 | 267 | ||
| 850 | 34 | 267 | ||
| 900 | 36 | 267 | ||
| 950 | 38 | 305 | ||
| 1000 | 40 | 305 | ||
| 1050 | 42 | 305 | ||
| 1100 | 44 | 343 | ||
| 1150 | 46 | 343 | ||
| 1200 | 48 | 343 | ||
| D(inch) | DN | OD | SCH5s | SCH10s | SCH10 | SCH20 | SCH30 | SCH40s | STD | SCH40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8" | 6 | 10.3 | - | 1.24 | 1.73 | 1.73 | 1.73 | |||
| 1/4" | 8 | 13.7 | - | 1.65 | - | - | - | 2.24 | 2.24 | 2.24 |
| 3/8" | 10 | 17.1 | - | 1.65 | - | - | - | 2.31 | 2.31 | 2.31 |
| 1/2" | 15 | 21.3 | 1.65 | 2.11 | - | - | - | 2.77 | 2.77 | 2.77 |
| 3/4" | 20 | 26.7 | 1.65 | 2.11 | - | - | - | 2.87 | 2.87 | 2.87 |
| 1" | 25 | 33.4 | 1.65 | 2.77 | - | - | - | 3.38 | 3.38 | 3.38 |
| 11/4" | 32 | 42.2 | 1.65 | 2.77 | - | - | - | 3.56 | 3.56 | 3.56 |
| 11/2" | 40 | 48.3 | 1.65 | 2.77 | - | - | - | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.68 |
| 2" | 50 | 60.3 | 1.65 | 2.77 | - | - | - | 3.91 | 3.91 | 3.91 |
| 21/2" | 65 | 73 | 2.11 | 3.05 | - | - | - | 5.16 | 5.16 | 5.16 |
| 3" | 80 | 88.9 | 2.11 | 3.05 | - | - | - | 5.49 | 5.49 | 5.49 |
| 31/2" | 90 | 101.6 | 2.11 | 3.05 | - | - | - | 5.74 | 5.74 | 5.74 |
| 4" | 100 | 114.3 | 2.11 | 3.05 | - | - | - | 6.02 | 6.02 | 6.02 |
| 5" | 125 | 141.3 | 2.77 | 3.4 | - | - | - | 6.55 | 6.55 | 6.55 |
| 6" | 150 | 168.3 | 2.77 | 3.4 | - | - | - | 7.11 | 7.11 | 7.11 |
| 8" | 200 | 219.1 | 2.77 | 3.76 | - | 6.35 | 7.04 | 8.18 | 8.18 | 8.18 |
| 10" | 250 | 273.1 | 3.4 | 4.19 | - | 6.35 | 7.8 | 9.27 | 9.27 | 9.27 |
| 12" | 300 | 323.9 | 3.96 | 4.57 | - | 6.35 | 8.83 | 9.53 | 9.53 | 10.31 |
| 14" | 350 | 355.6 | 3.96 | 4.78 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 9.53 | - | 9.53 | 11.13 |
| 16" | 400 | 406.4 | 4.19 | 4.78 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 9.53 | - | 9.53 | 12.7 |
| 18" | 450 | 457.2 | 4.19 | 4.78 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 11.13 | - | 9.53 | 14.27 |
| 20" | 500 | 508 | 4.78 | 5.54 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 12.7 | - | 9.53 | 15.09 |
| 22" | 550 | 558.8 | 4.78 | 5.54 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 12.7 | - | 9.53 | |
| 24" | 600 | 609.6 | 5.54 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 14.27 | - | 9.53 | 17.48 |
| 26" | 650 | 660.4 | - | - | 7.92 | 12.7 | - | - | 9.53 | - |
| 28" | 700 | 711.2 | - | - | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | - | 9.53 | - |
| 30" | 750 | 762 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | - | 9.53 | - |
| 32" | 800 | 812.8 | - | - | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | - | 9.53 | 17.48 |
| 34" | 850 | 863.6 | - | - | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | - | 9.53 | 17.48 |
| 36" | 900 | 914.4 | - | - | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | - | 9.53 | 19.05 |
| 38" | 950 | 965.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | - |
| 40" | 1000 | 1016 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | - |
| 42" | 1050 | 1066.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | - |
| 44" | 1100 | 1117.6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | - |
| 46" | 1150 | 1168.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | - |
| 48" | 1200 | 1219.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.53 | - |
Pipe fitting dimensions are in either metric or Standard English. Because pipe fitting covers Pipe Fitting Dimensions several aspects, only the most common pipe fitting sizes can be given here. The most applied version is the 90° long radius and the 45° elbow, while the 90° short radius elbow is applied if there is too little space. The function of a 180° elbow is to change direction of flow through 180°. Both, the LR and the SR types have a center to center dimension double the matching 90° elbows. These fittings will generally be used in furnesses or other heating or cooling units.
Some of the standards that apply to buttwelded fittings are listed below. Many organizations such as ASME, ASTM, ISO, MSS, etc. have very well developed standards and specifications for buttwelded fittings. It is always up to the designer to ensure that they are following the applicable standard and company specification, if available, during the design process.
Some widely used pipe fitting standards are as follows:
ASME: American Society for Mechanical Engineers
This is one of the reputed organizations in the world developing codes and standards.
The schedule number for pipe fitting starts from ASME/ANSI B16. The various classifications of ASME/ANSI B16 standards for different pipe fittings are as follows:
ASTM International: American Society for Testing and Materials
This is one of the largest voluntary standards development organizations in the world. It was originally known as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
AWWA: American Water Works Association
AWWA About – Established in 1881, the American Water Works Association is the largest nonprofit, scientific and educational association dedicated to managing and treating water, the world’s most important resource.
ANSI: The American National Standards Institute
ANSI is a private, non-profit organization. Its main function is to administer and coordinate the U.S. voluntary standardization and conformity assessment system. It provides a forum for development of American national standards. ANSI assigns “schedule numbers”. These numbers classify wall thicknesses for different pressure uses.
MSS STANDARDS: Manufacturers Standardization Society
The Manufacturers Standardization Society (MSS) of the Valve and Fittings Industry is a non-profit technical association organized for development and improvement of industry, national and international codes and standards for: Valves, Valve Actuators, Valve Modification, Pipe Fittings, Pipe Hangers, Pipe Supports, Flanges and Associated Seals
Difference between “Standard” and “Codes”:
Piping codes imply the requirements of design, fabrication, use of materials, tests and inspection of various pipe and piping system. It has a limited jurisdiction defined by the code. On the other hand, piping standards imply application design and construction rules and requirements for pipe fittings like adapters, flanges, sleeves, elbows, union, tees, valves etc. Like a code, it also has a limited scope defined by the standard.
Factors affecting standards: “Standards” on pipe fittings are based on certain factors like as follows:
BSP: British Standard Pipe
BSP is the U.K. standard for pipe fittings. This refers to a family of standard screw thread types for interconnecting and sealing pipe ends by mating an external (male) with an internal (female) thread. This has been adopted internationally. It is also known as British Standard Pipe Taper threads (BSPT )or British Standard Pipe Parallel (Straight) threads (BSPP ). While the BSPT achieves pressure tight joints by the threads alone, the BSPP requires a sealing ring.
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
This is the Japanese industrial standards or the standards used for industrial activities in Japan for pipe, tube and fittings and published through Japanese Standards Associations.
NPT: National Pipe Thread
National Pipe Thread is a U.S. standard straight (NPS) threads or for tapered (NPT) threads. This is the most popular US standard for pipe fittings. NPT fittings are based on the internal diameter (ID) of the pipe fitting.
BOLTS & NUTS
We are manufacturer of Flange bolts & Nuts and supply high quality
AN: Here, “A” stands for Army and “N” stands for Navy
The AN standard was originally designed for the U.S. Military. Whenever, a pipe fitting is AN fittings, it means that the fittings are measured on the outside diameter of the fittings, that is, in 1/16 inch increments.
For example, an AN 4 fitting means a fitting with an external diameter of approximately 4/16″ or ¼”. It is to be noted that approximation is important because AN external diameter is not a direct fit with an equivalent NPT thread.
Dash (-) size
Dash size is the standard used to refer to the inside diameter of a hose. This indicates the size by a two digit number which represents the relative ID in sixteenths of an inch. This is also used interchangeably with AN fittings. For example, a Dash “8” fitting means an AN 8 fitting.
ISO: International Organization for Standardization
ISO is the industrial pipe, tube and fittings standards and specifications from the International Organization for Standardization. ISO standards are numbered. They have format as follows:
“ISO[/IEC] [IS] nnnnn[:yyyy] Title” where
Pipe fittings are measured by their diameter, wall thickness (known as “schedule”), and shape or configuration. (Fittings are also defined by their material grade and whether they are welded or seamless.)
Diameter refers to outside diameter of a pipe or fitting.
The North American standard is known as Nominal Pipe Size (NPS). The International Standard is known as Diameter Nominal (DN). Pipes and fittings are actually made in similar sizes around the world: they are just labeled differently.
From ½ in to 12 inch “Nominal Pipe Size”, outside diameters are slightly larger than indicated size; inside diameters get smaller as schedules grow.
From 14 in and larger “Nominal Pipe Size”, outside diameters are exactly as indicated size; inside diameters get smaller as schedules grow.
As with other North American standards (inch, foot, yard, mile, …), many pipe standards (diameters up to 12 inch and wall thickness) are based on historical precedents (a toolmaker’s dies during US Civil War) rather than a “scientific” method.
The schedule numbers are used by the ANSI (American National Standards Institute) to denote wall thickness. The schedule numbers encompass all pipe dimensions beginning at NPS 1/8” up NPS 36”. Note that this configuration is only for fittings that match with a particular ANSI schedule number.
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) is a North American set of standard sizes for pipes used for high or low pressures and temperatures.
What does “schedule” mean for pipe fittings?
Schedule, often shortened as SCH, is a North American standard that refers to wall thickness of a pipe or pipe fitting.
What is schedule 40, SCH80?
Higher schedules mean thicker walls that can resist higher pressures.
Pipe standards define these wall thicknesses: SCH 5, 5S, 10, 10S, 20, 30, 40, 40S, 60, 80, 80S, 100, 120, 140, 160, STD, XS and XXS.
(S following a number is for stainless steel. Sizes without an S are for carbon steel.)
Higher schedules are heavier, require more material and are therefore more costly to make and install.
| Standard | Specification |
|---|---|
| ASTM A234 | Standard Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Moderate and High Temperature Service |
| ASTM A420 | Standard Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Low-Temperature Service |
| ASTM A234 WPB | ASTM A234 is Standard Specification for steel pipe fittings includes carbon and alloy steel material for moderate and high temperature services. WPB is one of the steel grade in this standard |
| ASME B16.9 | ASME B16.9 Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200). |
| ASME B16.28 | ASME B16.28 Standard covers ratings, overall dimensions, testing, tolerances, and markings for wrought carbon and alloy steel buttwelding short radius elbows and returns. |
| MSS SP-97 | MSS SP-97 Standard Practice covers essential dimensions, finish, tolerances, testing, marking, material, and minimum strength requirements for 90 degree integrally reinforced forged branch outlet fittings of buttwelding, socket welding, and threaded types. |
| ASTM A403 | Standard Specification for Wrought Austenitic Stainless Steel Piping Fittings. |
| DIN | EN | ASME |
|---|---|---|
| St 35.8 I St 35.8 III 15 Mo 3 13 CrMo 4 4 10 CrMo 9 10 St 35 N St 52.0 St 52.4 | P235GH-TC1 P235GH-TC2 16Mo3 13CrMo4-5 10CrMo9-10 X10CrMoVNb9-1 P215NL P265NL L360NB L360NE P355N P355NL1 P355NH | WPB WPL6 WPL3 WPHY 52 WP11 WP22 WP5 WP9 WP91 WP92 |
ASTM A234/ASME SA234M standard specification for piping fittings of wrought carbon steel and alloy steel for moderate and high temperature service.
| Grade | Type | C | Si | S | P | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Other | ób | ós | δ5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPB | 0.3 | 0.1min | 0.058 | 0.05 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | V:0.06;Nb:0.02 | 415-585 | 240 | 22 | 197 |
| WPC | 0.35 | 0.1min | 0.058 | 0.05 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | V:0.06;Nb:0.02 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 |
| WP1 | 0.28 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.9 | 0.44-0.65 | 380-550 | 205 | 22 | 197 | |||
| WP12 CL1 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.6 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 220 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP12 CL2 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.6 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL1 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5-1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL2 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.8 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL3 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.8 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP22 CL1 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP22 CL3 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP5 CL1 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 4-6 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP5 CL3 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 4-6 | 0.44-0.65 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP9 CL1 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-10 | 0.9-1.1 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP9 CL3 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-10 | 0.9-1.1 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WPR | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.045 | 0.4-1.06 | 1.6-2.24 | 435-605 | 315 | 22/28 | 217 | ||||
| WP91 | 0.08-0.12 | 0.2-0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-9.5 | 0.4 | 0.85-1.05 | See sdandard | 585-760 | 415 | 20 | 248 |
| WP911 | 0.09-0.13 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 8.5-10.5 | 0.4 | 0.9-1.1 | See sdandard | 620-840 | 440 | 20 | 248 |
| Tensile Requirements | WPB | WPC, WP11CL2 | WP11CL1 | WP11CL3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min, ksi[MPa] (0.2% offset or 0.5% extension-under-load) | 60-85 [415-585] | 70-95 [485-655] | 60-85 [415-585] | 75-100 [520-690] |
| Yield Strength, min, ksi[MPa] | 32 [240] | 40 [275] | 30 [205] | 45 [310] |
ASTM A403 Standard specification covers the standard for wrought austenitic stainless steel fittings for pressure piping applications.
| Steel No. | Type | C | Si | S | P | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Other | ób | ós | δ5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP304 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-11 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP304H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-11 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP304L | 0.035 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-13 | 485 | 170 | 28 | |||
| WP304LN | 0.03 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-10.5 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP304N | 0.08 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-11 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 550 | 240 | 28 | ||
| WP309 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 22-24 | 12-15 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP310 | 0.15 | 1.5 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 24-26 | 19-22 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP316 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP316H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP316LN | 0.03 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 11-14 | 2-3 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |
| WP316L | 0.035 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 10-16 | 2-3 | 485 | 170 | 28 | ||
| WP316N | 0.08 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 11-14 | 2-3 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 550 | 240 | 28 | |
| WP317 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 11-15 | 3-4 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP317L | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 11-15 | 3-4 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP321 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ti:5C-0.7 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP321H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ti:4C-0.7 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP347 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Nb+Ta:10C-1.1 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP347H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Nb+Ta:8C-1 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP348 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ta:0.1 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP348H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ta:0.1 | 515 | 205 | 28 |
| Grade | UNS | Tensile Strength, min | Yield Strength,min | Elongation min % in 4D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | Longit % | Trans% | ||
| ALL | ALL | 75 | 515 | 30 | 205 | 28 | 20 |
| 304L | S30403 | 70 | 485 | 25 | 170 | 28 | 20 |
| 316L | S31603 | 70 | 485 | 25 | 170 | 28 | 20 |
| 304N | S30451 | 80 | 550 | 35 | 240 | 28 | 20 |
| 316N | S31651 | 80 | 550 | 35 | 240 | 28 | 20 |
| S31726 | 80 | 550 | 35 | 240 | 28 | 20 | |
| XM-19 | S20910 | 100 | 690 | 55 | 380 | 28 | 20 |
| S31254 | 94-119 | 650-820 | 44 | 300 | 28 | 20 | |
| S34565 | 115 | 795 | 60 | 415 | 28 | 20 | |
| S33228 | 73 | 500 | 27 | 185 | 28 | 20 | |
Material Furnished to this specification shall conform to the requirements of specifications A960/A960M including any supplementary requirements that are indicates in the purchase order. Failure to company with the common requirements of Specification A960/A960M constitutes non-conformance with this specification . In case of conflict between this specification and Specification A960/A960M , this specification shall prevail.
ASTM A420/A420M-07 standard specification for piping fittings of wrought carbon steel and alloy steel for low-temperature service.
| Elements | WPL6, % | WPL9, % | WPL3, % | WPL8, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon [C] | ≤0.30 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.13 |
| Manganese [Mn] | 0.50-1.35 | 0.40-1.06 | 0.31-0.64 | ≤0.90 |
| Phosphorus [P] | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.030 |
| Sulfur [S] | ≤0.040 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.030 |
| Silicon [Si] | 0.15-0.40 | … | 0.13-0.37 | 0.13-0.37 |
| Nickel [Ni] | ≤0.40 | 1.60-2.24 | 3.2-3.8 | 8.4-9.6 |
| Chromium [Cr] | ≤0.30 | ... | ... | ... |
| Molybdenum [Mo] | ≤0.12 | ... | ... | ... |
| Copper [Cu] | ≤0.40 | 0.75-1.25 | … | … |
| Columbium [Cb] | ≤0.02 | ... | ... | ... |
| Vanadium[V] | ≤0.08 | ... | ... | ... |
| ASTM A420/ A420M | Tensile Strength, min. | Yield Strength, min. | Elongation %, min | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | Longitudinal | Transverse |
| WPL6 | 65-95 | 415-655 | 35 | 240 | 22 | 12 |
| WPL9 | 63-88 | 435-610 | 46 | 315 | 20 | … |
| WPL3 | 65-90 | 450-620 | 35 | 240 | 22 | 14 |
| WPL8 | 100-125 | 690-865 | 75 | 515 | 16 | … |
ASTM A234 is Standard Specification for steel pipe fittings includes carbon and alloy steel material for moderate and high temperature services.
ASME B16.9 Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200).
| Nominal | Outside Diameter | 90° Elbows | 45° Elbows | 180° Returns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size | Long Radius | Short Radius | Long Radius | Long Radius | ||||
| (inches) | (mm) | (inches) | Center to Face | Center to Face | Center to Face | Radius | Center to Center | Back to face |
| (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | |||
| 1/2 | 21.3 | 0.84 | 1.5 | – | 5/8 | 2 | 1.875 | |
| 3/4 | 26.7 | 1.05 | 1.125 | – | 7/16 | 2.25 | 1.6875 | |
| 1 | 33.4 | 1.315 | 1.5 | 1 | 7/8 | 3 | 2.1875 | |
| 1.25 | 42.2 | 1.66 | 1.875 | 1.25 | 1 | 3.75 | 2.75 | |
| 1.5 | 48.3 | 1.9 | 2.25 | 1.5 | 1.125 | 3 | 4.5 | 3.25 |
| 2 | 60.3 | 2.375 | 3 | 2 | 1.375 | 4 | 6 | 4.1875 |
| 2.5 | 73 | 2.875 | 3.75 | 2.5 | 1.75 | 5 | 7.5 | 5.1875 |
| 3 | 88.9 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 3.5 | 101.6 | 4 | 5.25 | 3.5 | 2.25 | 7 | 10.5 | 7.25 |
| 4 | 114.3 | 4.5 | 6 | 4 | 2.5 | 8 | 12 | 8.25 |
| 5 | 141.3 | 5.563 | 7.5 | 5 | 3.125 | 10 | 15 | 10.3125 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 6.625 | 9 | 6 | 3.75 | 12 | 18 | 12.3125 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 8.625 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 12 | 24 | 16.3125 |
| 10 | 273.1 | 10.75 | 15 | 10 | 6.25 | 15 | 30 | 20.375 |
| 12 | 323.9 | 12.75 | 18 | 12 | 7.5 | 18 | 36 | 24.375 |
| NOMINAL PIPE SIZE NPS | ANGULARITY TOLERANCES | ANGULARITY TOLERANCES |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Off Angle Q | Off Plane P |
| ½ to 4 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| 5 to 8 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| 10 to 12 | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| 14 to 16 | 0.09 | 0.25 |
| 18 to 24 | 0.12 | 0.38 |
| 26 to 30 | 0.19 | 0.38 |
| 32 to 42 | 0.19 | 0.5 |
| 44 to 48 | 0.18 | 0.75 |
MSS SP-97 Standard Practice covers essential dimensions, finish, tolerances, testing, marking, material, and minimum strength requirements for 90 degree integrally reinforced forged branch outlet fittings of buttwelding, socket welding, and threaded types.
| Nominal wall Thickness : t | End Preparation |
|---|---|
| t<5mm (for austenitic alloy steel t<4mm) | Cut square or slightly chamfer at manufacturer ‘ s option |
5| Plain Bevel as in sketch ( a ) above |
|
| t>22mm | Compound Bevel as in sketch ( b ) above |
| Elements | Value, % |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | ≤0.30 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤1.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤0.035 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤0.035 |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤0.50 |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤0.50 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤0.50 |
| Chromium (Cr) | ≤0.25 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | ≤0.13 |
| Vanadium (V) | ≤0.13 |
| Columbium (Cb) | ≤0.10 |
| Titanium(Ti) | ≤0.05 |
For packing of carbon steel flanges with painting,we would use the bubble wrap to protect the painting.For flanges without painting or oiled with long-term shipment,we would suggest client to use the anti-tarnish paper and plastic bag to prevent the rust.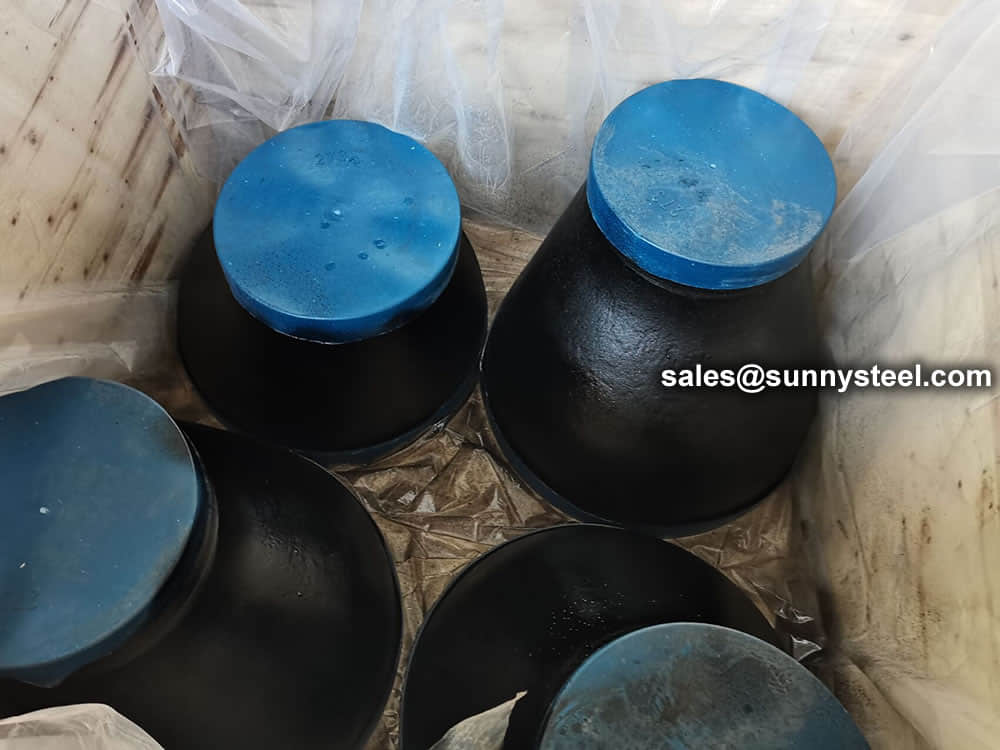  Packing reducers in wooden cases
Packing reducers in wooden cases


Wrap the plastic tightly around the pipe to protect the tee

Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time? A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment. Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free? A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee. Q: What are your payment terms? A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment Q: What is the packaging and transportation form? A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea. Q: What is your minimum order quantity? A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.