Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199
Our team is highly trained and experienced in servicing and producing all types of steel supplies. Need help or have a question?
sales@abrasionresistantpipe.com
Tel.: +8621-3378-0199

Type 316L is the low carbon version of 316 stainless. With the addition of molybdenum, the steel is popular for use in severe corrosion environments due to the materials immunity from boundary carbide precipitation (sensitisation). The material is widely used in heavy gauge welded components and weld annealing is only required where the material is for use in high stress environments. 316L has an extensive variety of uses especially in marine applications due to the materials high corrosion resistance.
Type 316L is the low carbon version of 316 stainless. With the addition of molybdenum, the steel is popular for use in severe corrosion environments due to the materials immunity from boundary carbide precipitation (sensitisation).
The material is widely used in heavy gauge welded components and weld annealing is only required where the material is for use in high stress environments. 316L has an extensive variety of uses especially in marine applications due to the materials high corrosion resistance.
| Grade | Scope | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | Min | - | - | - | 0 | - | 16 | 2 | 10 | - |
| Max | 0.08 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 18 | 3 | 14 | 0.1 | |
| 316L | Min | - | - | - | - | - | 16 | 2 | 10 | - |
| Max | 0.03 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 18 | 3 | 14 | 0.1 | |
| 316H | Min | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0 | - | - | 16 | 2 | 10 | - |
| max | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 18 | 3 | 14 | - |
| Grade | Tensile Str | Yield Str 0.2% Proof | Elong | Hardness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) min | (MPa) min | (% in 50mm) min | Rockwell B (HR B) max | Brinell (HB) max | |
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 95 | 217 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 95 | 217 |
| 316H | 515 | 205 | 40 | 95 | 217 |
The high levels of chromium and nickel found in 304 and 316 stainless steel provides them with a strong resistance to heat, abrasion, and corrosion. Not only are they known for their resistance to corrosion, they are also known for their clean appearance and overall cleanliness.
Both types of stainless steel appear in wide-ranging industries. As the most common grade of stainless steel, 304 is considered the standard “18/8” stainless. 304 stainless steel is widely used because it is durable and easy to form into various forms such as stainless steel sheet, stainless steel plate, stainless steel bar, and stainless steel tube. 316 steel’s resistance to chemicals and marine environments makes it a popular choice among manufacturers.
Heat Resistance
Heat resistance is an important factor to consider when comparing the different grades of stainless steel. The melting range of 304 is around 50 to 100 degrees Fahrenheit higher than 316. Although the melting range of 304 is higher than 316, they both have good resistance to oxidization in intermittent service up to 870°C (1500℉) and in continuous service at 925°C (1697℉).
304 SS: Handles high heat well, but continuous use at 425-860 °C (797-1580 °F) may cause corrosion.
316 SS: Performs best in temperatures above 843 ℃ (1550 ℉) and below 454 ℃ (850°F)
Price
What makes 316 more expensive than 304 stainless steel? The increase of nickel content and the addition of molybdenum in 316 makes it more expensive than 304. On average, the price of 316 stainless steel 40% higher than the price of 304 SS.
Which is Better?
When comparing 304 stainless steel vs 316, they both have pros and cons to consider when deciding which one to use for different applications. For instance, 316 stainless steel is more resistant than 304 to salt and other corrosives. So, if you are manufacturing a product that will often face exposure to chemicals or a marine environment, 316 is the better choice.
On the other hand, if you are manufacturing a product that does not need strong corrosion resistance, 304 is a practical and economical choice. For many applications, 304 and 316 are actually interchangeable.
| 316 | 316L |
|---|---|
| ASTM A240 | ASTM A240 |
| ASTM A666 | ASTM A666 |
| ASME SA240 | ASME SA240 |
| AMS 5524 | AMS 5507 |
The reality is there are many nuances associated with steel plate and failure to understand them will result in many problems throughout its use in a project. The information in this eBook is meant to clear up many misconceptions.
Carbon steel plate is manufactured for a variety of applications based on its carbon content. Low carbon steel plate, depending on its thickness offers characteristics such as maximum cold forming capability, weldability and improved machining. Medium carbon steel plates (.40 – .50) that are silicon killed offers better strength capabilities but have limited machining and welding properties.
Other types of steel plate offer benefits for structure and construction applications, resistance to abrasion, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Additionally, steel plate coils are available in low carbon, pickled and oiled, and black steel coils used for precision roller leveling. It may also be used for cutting standard and custom lengths up to 480”.
As there are different sizes, there are different types of steel plate: stainless steel (commonly known), high-carbon, low-carbon, or alloy steel plates. Each of these types of steel plate are used for different applications, some may be household items while others are much larger, like buildings or tanks.
| Abbreviation | Full description |
|---|---|
| ASTM International | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| ANSI | American National Standards Institute |
| AISC | American Institute of Steel Construction |
| AISI | American Iron & Steel Institute |
| ASCE | American Society of Civil Engineers |
| ASME | American Society of Mechanical Engineers |
| AWS | American Welding Society |
Shipbuilding steel plates are produced under the approval of production methods of classification societies in different countries refers to offshore and marine steels.
Iron and carbon are the most abundant materials present in steel. Pure iron is not particularly strong or hard on its own, so it is the addition of carbon that helps give steel its great strength.
The crude iron used to produce steel has a relatively high amount of carbon. Its carbon composition can be as high as 2.1%, which is the greatest amount of carbon a material can contain and still be considered steel.
However, iron can be processed further to reduce carbon. This manipulation of carbon alters several material properties, including:
Strength: The load a material can bear, measured by yield point and tensile strength. Yield point is the point at which a material deforms, but does not break, and tensile strength is the amount of stress needed to actually break a material.
Ductility: The amount a material can be stretched without becoming brittle. Ductility is measured by elongation, which is the percent the length of a material increases before it breaks.
Hardness: The wear resistance of material and machinability of material. This is usually measured on the Rockwell hardness scale or Brinell Hardness scale.
The carbon present in steel is typically reduced so that it fits into three main categories of carbon steel: low (or mild), medium and high carbon steel. Each of these categories contain different levels of carbon, show in the chart below.| Type of carbon steel | Carbon composition |
|---|---|
| Low carbon/mild | 0.05-0.25% |
| Medium carbon | 0.26-0.60% |
| High carbon | 0.61-1.50% |
Carbon steel plate almost include all the common standards of steel plate/sheet.
So carbon steel plates have a widely coverage for different types of steel plates in different industries.
Also known as mild steel, low carbon steel has low strength relative to steel with higher carbon levels. Low carbon steel is the most ductile – or machinable – type of carbon steel as well.
Chemical alloys can also be added to low carbon steel to enhance desired properties without increasing the material’s weight. For example, if low carbon steel requires greater hardness for its desired application, manganese can be added to increase hardness without adding weight. Low carbon steel that contains additional alloys is typically referred to as high strength, low alloy (HSLA) steel.
Some of the most common low carbon steel plate grades, all stocked by us, include ASTM A36, A572 Grades 42 & 50 and A830-1020. Each of these grades have moderate strength, high ductility and lighter weight due to the low carbon content and addition of other alloys. These properties make low carbon steel ideal for use in structural applications like building construction, bridges and transmission towers, where materials must be able to withstand high stress while also being easy to form into structural shapes.
Medium carbon steel provides a balance between low and high carbon steel, offering greater strength and hardness than low carbon steel while still remaining more ductile than high carbon steel. Medium carbon steel also typically contains other alloys, such as manganese, that also contribute to its properties.
In applications where greater toughness and hardness are required, medium carbon steel plate can receive heat treatments – such as quenching and tempering – that enhance these properties without compromising its machinability.
Quenching and tempering is a two-step heat treatment process. In the quenching step of this process, steel is heated to a temperature between 1,500-and 1,650-degrees Fahrenheit, then rapidly cooled with water. In the tempering step, the steel is then re-heated to a below-critical temperature – between 300 and 700 degrees – and air-cooled. This process alters the crystal grain structure of steel to enhance hardness and other mechanical properties.
Two common medium carbon steel plate grades that stocks are ASTM A516 Grade 70 and A830-1045. The moderate carbon composition and additional alloys give these grades – and other medium carbon grades – a balance of strength, hardness, ductility and wear resistance. These properties make medium carbon steel ideal for use in applications where materials must withstand strong forces without breaking or wearing out, such as machine parts – including gears, axles and bolts – pressure vessel tanks and automotive parts and components.
| Standard | Steel Grade | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A36/A36M | A36 | |||
| ASTM A283/A283M | A283 Grade A | A283 Grade B | A283 Grade C | A283 Grade D |
| ASTM A514/A514M | A514 Grade A | A514 Grade B | A514 Grade C | A514 Grade E |
| A514 Grade F | A514 Grade H | A514 Grade J | A514 Grade K | |
| A514 Grade M | A514 Grade P | A514 Grade Q | A514 Grade R | |
| A514 Grade S | A514 Grade T | |||
| ASTM A572/A572M | A572 Grade 42 | A572 Grade 50 | A572 Grade 55 | A572 Grade 60 |
| A572 Grade 65 | ||||
| ASTM A573/A573M | A573 Grade 58 | A573 Grade 65 | A573 Grade 70 | |
| ASTM A588/A588M | A588 Grade A | A588 Grade C | A588 Grade K | A588 Grade B |
| ASTM A633/A633M | A633 Grade A | A633 Grade C | A633 Grade D | A633 Grade E |
| ASTM A656/A656M | A656 Grade 50 | A656 Grade 60 | A656 Grade 70 | A656 Grade 80 |
| ASTM A709/A709M | A709 Grade 36 | A709 Grade 50A573Grade70 | A709 Grade 50S | A709 Grade 50W |
| A709 Grade HPS50W | A709 Grade HPS70W | A709 Grade 100 | A709 Grade 100W | |
| A709 Grade HPS100W | ||||
| ASME SA36/SA36M | SA36 | |||
| ASME SA283/SA283M | SA283 Grade A | SA283 Grade B | SA283 Grade C | SA283 Grade D |
| ASME SA514/SA514M | SA514 Grade A | SA514 Grade B | SA514 Grade C | SA514 Grade E |
| SA514 Grade M | SA514 Grade P | SA514 Grade Q | SA514 Grade R | |
| SA514 Grade S | SA514 Grade T | |||
| ASME SA572/SA572M | SA572 Grade 42 | SA572 Grade 50 | SA572 Grade 55 | SA572 Grade 60 |
| SA572 Grade 65 | ||||
| ASME SA573/SA573M | SA573 Grade 58 | SA573 Grade 65 | SA573 Grade 70 | |
| ASME SA588/SA588M | SA588 Grade A | SA588 Grade B | SA588 Grade C | SA588 Grade K |
| ASME SA633/SA633M | SA633 Grade A | SA633 Grade C | SA633 Grade D | SA633 Grade E |
| ASME SA656/SA656M | SA656 Grade 50 | SA656 Grade 60 | SA656 Grade 70 | SA656 Grade 80 |
| ASME SA709/SA709M | SA709 Grade 36 | SA709 Grade 50 | SA709 Grade 50S | SA709 Grade 50W |
| SA709 Grade HPS50W | SA709 Grade HPS70W | SA709 Grade 100 | SA709 Grade 100W | |
| SA709 Grade HPS100W | ||||
| EN10025-2 | S235JR | S235J0 | S235J2 | S275JR |
| S275J0 | S275J2 | S355JR | S355J0 | |
| S355J2 | S355K2 | S420J0 | ||
| EN10025-3 | S275N | S275NL | S355N | S355NL |
| S420N | S420NL | S460N | S460NL | |
| EN10025-4 | S275M | S275ML | S355M | S420ML |
| S355ML | S460M | S420M | S460ML | |
| EN10025-6 | S460Q | S460QL | S460QL1 | S500Q |
| S500QL | S500QL1 | S550Q | S550QL | |
| S550QL1 | S620Q | S620QL | S620QL1 | |
| S690Q | S690QL | S890Q | S690QL1 | |
| S890QL | S890QL1 | S960Q | S960QL | |
| JIS G3101 | SS330 | SS400 | SS490 | SS540 |
| JIS G3106 | SM400A | SM400B | SM400C | SM490A |
| SM490B | SM490C | SM490YA | SM490YB | |
| SM520B | SM520C | SM570 | ||
| DIN 17100 | St37-2 | USt37-2 | RSt37-2 | St37-3 |
| St52-3 | ||||
| DIN 17102 | StE255 | WStE255 | TStE255 | EStE255 |
| StE285 | WStE285 | TStE285 | EStE285 | |
| StE315 | WStE315 | TStE315 | EStE315 | |
| StE355 | WStE355 | TStE355 | EStE355 | |
| StE380 | WStE380 | TStE380 | EStE380 | |
| StE420 | WStE420 | TStE420 | EStE420 | |
| StE460 | WStE460 | TStE460 | EStE460 | |
| StE500 | WStE500 | TStE500 | EStE500 | |
| GB/T700 | Q235A | Q235B | Q235C | Q235D |
| Q275 | ||||
| GB/T1591 | Q345A | Q345B | Q345C | Q345D |
| Q345E | Q390A | Q390B | Q390C | |
| Q390D | Q390E | Q420A | Q420B | |
| Q420C | Q420D | Q420E | Q460C | |
| Q460D | Q460E | |||
| GB/T16270 | Q460C | Q460D | Q460E | Q460F |
| Q500C | Q500D | Q500E | Q500F | |
| Q550C | Q550D | Q550E | Q550F | |
| Q620C | Q620D | Q620E | Q620F | |
| Q690C | Q690D | Q690E | Q690F | |
| Q800C | Q800D | Q800E | Q800F | |
| Q890C | Q890D | Q890E | Q890F | |
| Q960C | Q960D | Q960E | Q960F | |
| Standard | Steel Grade | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN10083-3 | 38Cr2 | 41CrS4 | 50CrMo4 | 51CrV4 |
| 46Cr2 | 25CrMo4 | 30CrNiMo8 | 20MnB5 | |
| 34Cr4 | 25CrMoS4 | 34CrNiMo6 | 30MnB5 | |
| 34CrS4 | 34CrMo4 | 35NiCr6 | 38MnB5 | |
| 37Cr4 | 34CrMoS4 | 36NiCrMo16 | 27MnCrB5-2 | |
| 37CrS4 | 42CrMo4 | 39NiCrMo3 | 33MnCrB5-2 | |
| 41Cr4 | 42CrMoS4 | 30NiCrMo16-6 | 39MnCrB6-2 | |
| GB/T 3077 | 20Mn2 | 20MnVB | 12CrMoV | 20CrNi |
| 30Mn2 | 40MnVB | 35CrMoV | 40CrNi | |
| 35Mn2 | 20MnTiB | 12Cr1MoV | 45CrNi | |
| 40Mn2 | 25MnTiBRE | 25Cr2MoVA | 50CrNi | |
| 45Mn2 | 15Cr | 25Cr2Mo1VA | 12CrNi2 | |
| 50Mn2 | 15CrA | 38CrMoAl | 12CrNi3 | |
| 20MnV | 20Cr | 40CrV | 20CrNi3 | |
| 27SiMn | 30Cr | 50CrVA | 30CrNi3 | |
| 35SiMn | 35Cr | 15CrMn | 37CrNi3 | |
| 42SiMn | 40Cr | 20CrMn | 12Cr2Ni4 | |
| 20SiMn2MoV | 45Cr | 40CrMn | 20Cr2Ni4 | |
| 25SiMn2MoV | 50Cr | 20CrMnSi | 20CrNiMo | |
| 37SiMn2MoV | 38CrSi | 25CrMnSi | 40CrNiMoA | |
| 40B | 12CrMo | 30CrMnSi | 18CrNiMnMoA | |
| 45B | 15CrMo | 30CrMnSiA | 45CrNiMoVA | |
| 50B | 20CrMo | 35CrMnSiA | 18Cr2Ni4WA | |
| 40MnB | 30CrMo | 20CrMnMo | 25Cr2Ni4WA | |
| 45MnB | 30CrMoA | 40CrMnMo | ||
| 20MnMoB | 35CrMo | 20CrMnTi | ||
| 15MnVB | 42CrMo | 30CrMnTi | ||
Quality stainless steel plates are useful in a wide range of industries as they are generally used in elevators, doors, windows, kitchen utensils, pressure vessels, and much more. This product’s formability, longevity, and resistance to corrosion makes it perfect.
| Grade | C(%) | Si(%) | Mn(%) | P(%) | S(%) | Ni(%) | Cr(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 8.0~10.5 | 18.0~20.0 |
| 304L | 0.03 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 8.0~12.0 | 18.0~20.0 |
| 316 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 10.0~14.0 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 10.0~14.0 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 316Ti | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 10.0~14.0 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 321 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 9.0~12.0 | 17.0~19.0 |
| 317L | 0.03 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 11.0~15.0 | 18.0~20.0 |
| 310S | 0.08 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.0452 | 0.03 | 19.0~22.0 | 24.0~26.0 |
| 347 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 9.0~13.0 | 17.0~19.0 |
| S31803 | 0.03 | 1 | 2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 4.5~6.5 | 21.0~23.0 |
| S32205 | 0.03 | 1 | 2 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 4.5~6.5 | 22.0~23.0 |
| S32750 | 0.03 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 0.035 | 0.02 | 6.0~8.0 | 24.0~26.0 |
| 904L | 0.02 | 1 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.035 | 23.0~28.0 | 19.0~23.0 |
| 254SMo | 0.02 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 17.5~18.5 | 19.5~20.5 |
| 17-4PH | 0.07 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 3.0~5.0 | 15.0~17.5 |
| 253MA | 0.05~0.01 | 1.4~2.2 | 2 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 10.0~12.0 | 20.0~22.0 |
| 301 | 0.15 | 1 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 6.0~8.0 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 302 | 0.15 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 8.0~10.0 | 17.0~19.0 |
| 304N | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 8.0~10.5 | 18.0~20.0 |
| 304H | 0.04~0.1 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 8.0~10.5 | 18.0~20.0 |
| 309S | 0.08 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 12.0~15.0 | 22.0~24.0 |
| 310H | 0.04~0.1 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 19.0~22.0 | 24.0~26.0 |
| 316LN | 0.03 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 10.0~14.0 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 316H | 0.04~0.1 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 10.0~14.0 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 321H | 0.04~0.1 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 9.0~12.0 | 17.0~19.0 |
| 347H | 0.04~0.1 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 9.0~13.0 | 17.0~19.0 |
| S32760 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 6.0~8.0 | 24.0~26.0 |
| S32304 | 0.03 | 1 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 3.0~5.5 | 21.5~24.5 |
| s32550 | 0.04 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 4.5~6.5 | 24.0~27.0 |
| S32900 | 0.08 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 2.0~5.0 | 23.0~28.0 |
| S32950 | 0.03 | 0.6 | 2 | 0.035 | 0.01 | 3.5~5.2 | 26.0~29.0 |
| 926 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 24.0~26.0 | 19.0~21.0 |
| 654SMo | 0.02 | 0.5 | 19.5~20.5 | 0.03 | 0.005 | 21.0~23.0 | 24.0~25.0 |
| 17-7PH | 0.08 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 6.0~7.7 | 16.0~18.0 |
| PH15-7Mo | 0.08 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 6.0~7.7 | 14.0~16.0 |
| 15-5PH | 0.07 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 3.5~5.5 | 14.0~15.5 |
| 410 | 0.08~0.15 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 11.5~13.5 |
| 410S | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.6 | 11.5~13.5 |
| 420 | 0.15 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | / | 12.0~14.0 |
| 420F | 0.3~0.4 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.06 | 0.2~0.34 | 0.5 | 12.5~14.0 |
| 431 | 0.2 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.25~2.5 | 15.0~17.0 |
| 440A | 0.6~0.75 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | / | 16.0~18.0 |
| 440B | 0.75~0.95 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | / | 16.0~18.0 |
| 440C | 0.95~1.20 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | / | 16.0~18.0 |
| 409(L) | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 10.5~11.7 |
| 430 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 16.0~18.0 |
| 434 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | / | 16.0~18.0 |
| 436 | 0.12 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | / | 16.0~18.0 |
| 439 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.5 | 17.0~19.0 |
| 444 | 0.25 | 1 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 17.5~19.5 |
 Steel Plate is both corrosion and abrasion-resistant. It is manufactured to a much broader range of thicknesses than ordinary steel sheets. Plate steel is primarily used in applications where a super-structural framework and indestructible durability are required. Not only is it produced for structural purposes, but it can also be implemented for general repairs too. In addition to great reinforcement purposes, Steel Plate is able to withstand immense stress from the harshest natural environments, mainly, the ocean. It serves as a considerable advantage to the world of heavy machinery. Its durability allows for machining and wearable elements to last much longer. Although it’s mostly used for reinforcement and bracing purposes, Plate Steel has proved to have a substantial degree of versatility.
Steel Plate is both corrosion and abrasion-resistant. It is manufactured to a much broader range of thicknesses than ordinary steel sheets. Plate steel is primarily used in applications where a super-structural framework and indestructible durability are required. Not only is it produced for structural purposes, but it can also be implemented for general repairs too. In addition to great reinforcement purposes, Steel Plate is able to withstand immense stress from the harshest natural environments, mainly, the ocean. It serves as a considerable advantage to the world of heavy machinery. Its durability allows for machining and wearable elements to last much longer. Although it’s mostly used for reinforcement and bracing purposes, Plate Steel has proved to have a substantial degree of versatility.
Steel plates can be manufactured by large steel factories or smaller, more specialized plants. Steel plates are one of the many types of steel that can be produced, other types include steel bars, sheets, slabs, rolls, and more. Steel plates are often used for structural and construction applications, pressure vessels, marine and offshore equipment, and military applications. The grade, elements and parameters of a steel plate are also important in how it is used. Construction The construction industry requires many types of steel in all sizes. Steel plates can be found in buildings, bridges and on construction vehicles. Pressure Vessel Plate Pressure vessel plate is a type of steel plate used for storage containers. These storage containers can be boilers, gas tanks, or any unit that stores compressed gas or fluid. They can be manufactured to hold contents at outdoor temperatures or hold contents are more extreme temperatures. Depending on the purpose, these steel plates can be course-grain or fine-grain. Marine Steel plates are also used extensively in the shipbuilding industry. The plates are used for ships and barges or oil rigs and other offshore equipment. They may be manufactured structural parts or they may be implemented as repair pieces. Sometimes extremely durable steel plates are needed, especially in the construction of large offshore facilities. Military Military steel plates are used in tanks, jeeps, trucks and ground vehicles, as well as helicopters, jets and other aircraft. The Navy uses this steel for shipbuilding and naval repair.
There are many reasons why stainless steel plates are used for a wide variety of applications and products. One main reason is because of its high resistance to oxidation and corrosion. It is also resistant to abrasion and is easy to clean. Stainless steel plates (and stainless steel in general) are also easy to form, has a clean and attractive appearance, and are relatively light yet very durable. These are also pretty malleable without compromising on strength, making it ideal for use with a lot of things. Stainless steel is used by a huge number of industries and by many businesses due to this versatility, strength and corrosion resistance. The usage of these plates often depends on the plate grade. With so many plate grades available, you can be sure that this particular metal does see itself being used for a huge number of applications. Similar to stainless steel plate, the sheet metal has high tensile strength, durability and delivers an exceptional finish. Stainless steel is thus ideal for food production and storage as it does not affect the flavour of the food and the corrosion resistance is an important factor when it comes into contact with acidic foods. Stainless steel is easily cleaned which keeps germs at bay, in turn maintaining the integrity of any sterile environment, including that of the medical industry. Stainless steel sheets, also commonly known as Cold Rolled Products, can be moulded into shapes for making cookware, such as grills, sinks, pots and cookers. Stainless steel sheet is popular as a finish for refrigerators, freezers, countertops and dishwashers. The sheet metal is available in flat pieces or coiled strips and is also useful when making licence plates for cars and even the base of light bulbs.
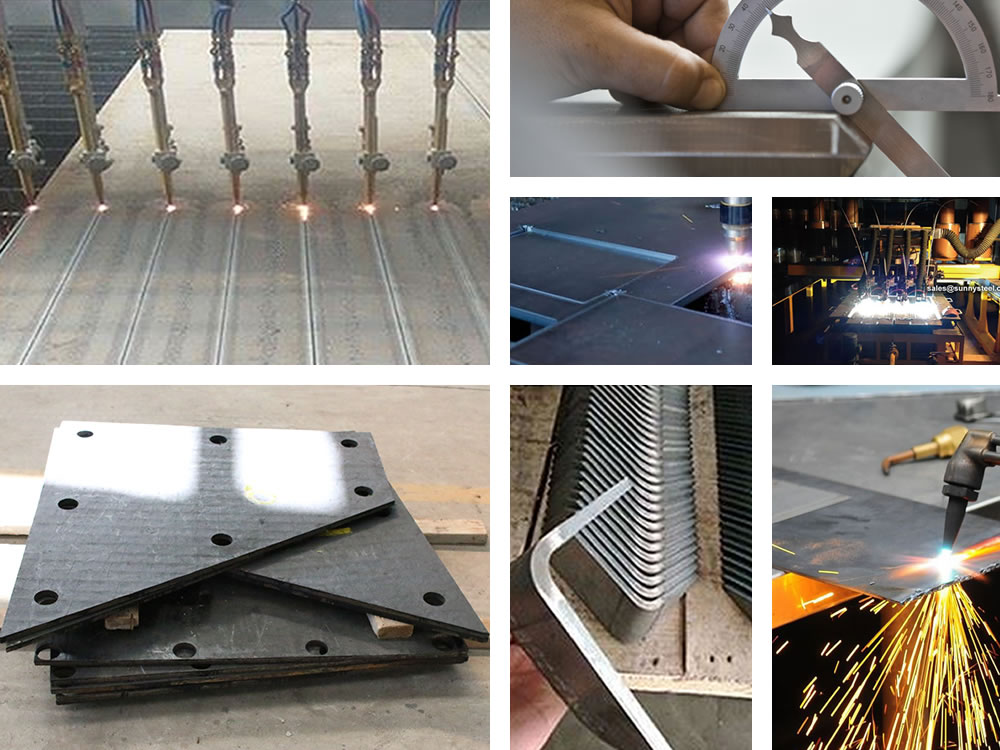 The processed product does not require further edge optimization, which greatly improves the customer’s production efficiency and reduces production costs.
The processed product does not require further edge optimization, which greatly improves the customer’s production efficiency and reduces production costs.
Laser cutting
Laser cutting is suitable for more complex and high-precision shape and contour materials, especially the cutting of thinner plates, so it is an ideal choice for processing high-end products.
Plasma Cutting
The working area can reach 3×5 meters, and it can cut stainless steel plates of various grades with a thickness of 3-150 mm. In most cases, the cutting needs to be performed underwater, so as to ensure the flatness and straightness of the final parts, while reducing the affected area.
Waterjet cutting
The tolerance of water jet cutting is small and the cutting surface is smooth. During the processing, there will be no oxidation of metal materials, no residual stress and heat-affected zone, avoiding secondary processing, which greatly saves time and manufacturing costs, and achieves the best economic benefits for customers.
Stable Job
Our factory use high-quality imported machine tools. When the machine tool is working, the table and the workpiece will not move. The laser head movement design with small inertia and high dynamic performance is adopted to greatly improve the accuracy and stability of the machine tool. Convenient exchange of tables reduces machine standby time and improves equipment utilization.
Automatic control
The automatic programming software that comes with the cutting machine directly generates the numerical control processing program from the graphic file. At the same time, the communication software can be used to make the CNC and the computer implement two-way communication, and the drawing on the computer is convenient and simple. Automatic nesting and discharging can improve the utilization rate and production efficiency of plates.
High-quality equipment performance
Imported pneumatic components ensure the correct function of the machine tool. Various orchestration can be automatically converted for cutting various materials and plate thicknesses. High-pressure auxiliary gas ensures clean cutting of stainless steel.
Bending
Final product of steel plate bending is U, V shape and channel steels, steel plate with ductile properties and small thickness size (steel sheet) is suitable for this processing, the core equipment is brake press.
Beveling
Plate beveling is essential for welding treatment, it removes the steel part from the steel edge to create a space for welding material. This processing makes the welding joint more firm for better penetration and deposition.
Pickling
The purpose of plate pickling is to remove impurities of the steel plate on the surface, steel workpiece in high temperature environment inevitably have a oxide layer on steel surface, by dipping in a kind of strong acidic pickle liquor, the impurities like stains, rust, inorganic contaminants and scale can all be cleaned.
Rolling
Hot rolling: hot rolling is the most common production process, final product is covered with rough oxide layer which can be removed in pickling process.
Cold rolling: cold rolling steel has advantages of better surface finish condition and strict tolerance, it can not be used to reducing the steel plate thickness.
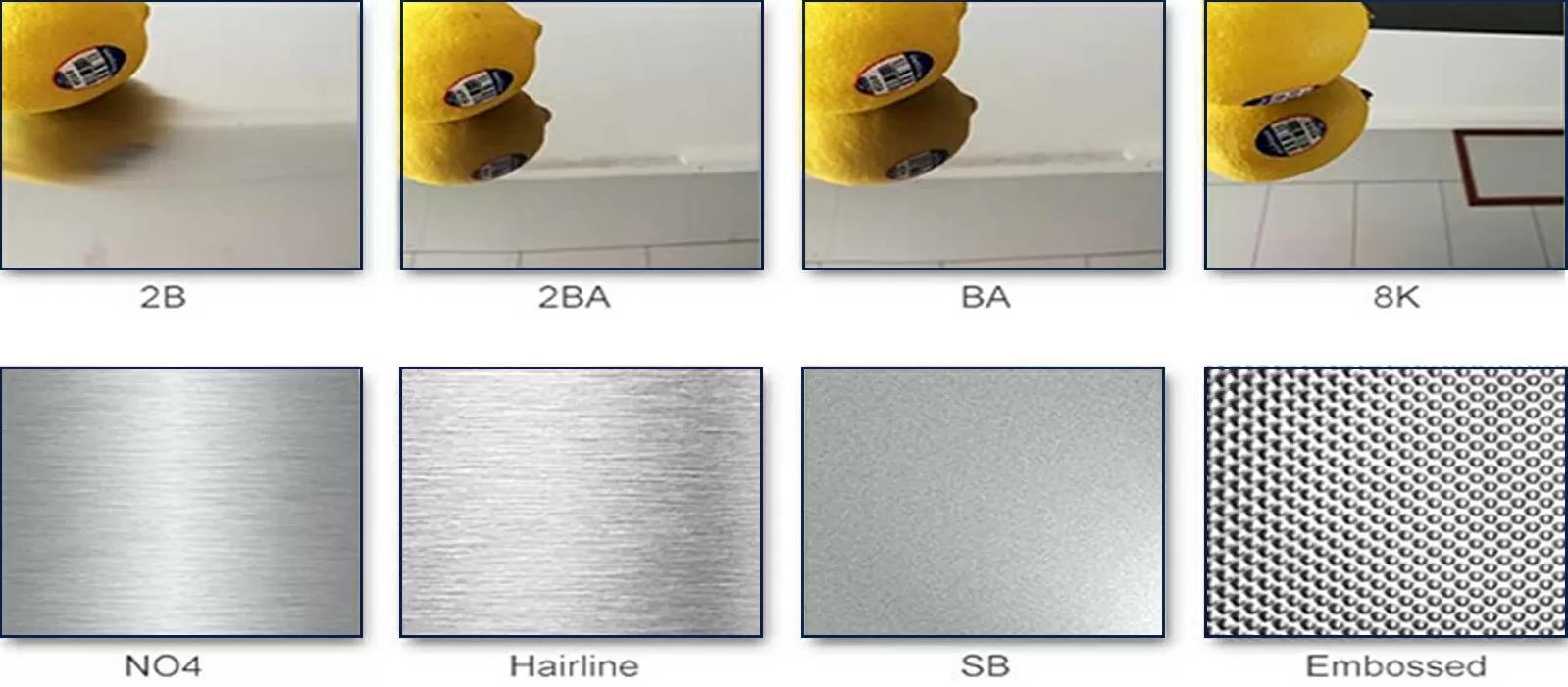

| Surface | Characteristic | Summary of manufacturing method | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO.1 | Silvery white lackluster | Hot rolled to specified thickness | Do not need to have a glossy surface use |
| NO.2D | Silvery white | After cold rolling, heat treatment and pickling are carried out | General material, deep material |
| NO.2B | Gloss is stronger than No.2D | After No.2D treatment, the final light cold rolling is carried out through the polishing roller | The general material |
| BA | As bright as a sixpence | No standard, but usually a bright annealed surface with high reflectivity. | Building materials, kitchen utensils |
| NO.3 | Rough lapping | Grind with 100~200# (unit) strop tape | Building materials, kitchen utensils |
| NO.4 | Intermediate grinding | Polished surface obtained by grinding with 150~180# strop abrasive tape | Building materials, kitchen utensils |
| NO.240 | Fine lapping | Grinding with 240# strop abrasive tape | kitchenware |
| NO.320 | Very fine grinding | Grinding was carried out with 320# strop abrasive tape | kitchenware |
| NO.400 | The luster is close to BA | Use 400# polishing wheel to grind | General timber, building timber, kitchen appliances |
| HL | Hairline grinding | Suitable particle material for hair stripe grinding (150~240#) with many grains | Building, construction material |
| NO.7 | It's close to mirror grinding | Use a 600# rotary polishing wheel to grind | For art or decoration |
| NO.8 | Mirror ultrafinish | The mirror is ground with a polishing wheel | Reflector, for decoration |
Hot rolled steel plate is basic steel plate product state, hot roll means processing temperature is over 1700˚F(re-crystallization temperature),at this temperature, steel forms even and stable structure, hot rolled steel plate can be fabricated easily, cutting, welding, etc, and it is more competitive for lower price than cold rolled steel plate. So knowing what kind of steel you need might help you reduce the cost.
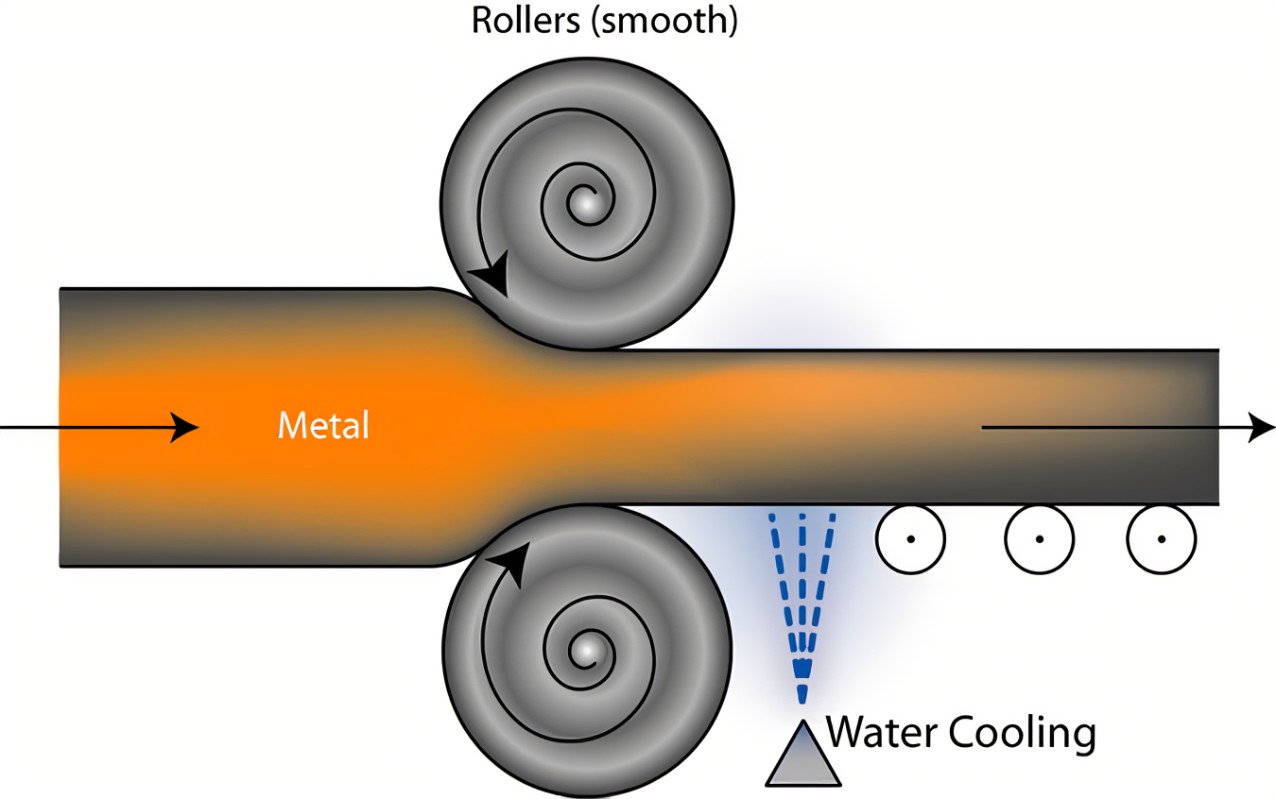
A steel billet is rolled after several passes after heating, and then trimmed to be corrected into a steel sheet. Hot rolling can significantly reduce energy consumption and reduce costs. Steel plasticity is active during hot rolling, and the deformation resistance is low, which means steel billet can be fabricated with lower energy consumption. With the high temperature, the coarse grains in the as-cast state are broken, the cracks are healed, the casting defects are reduced or eliminated, the as-cast microstructure is transformed into a deformed structure to improve the processing properties of the alloy. Then Steel plate size shrinks slightly. Unlike cold rolled steel plate, it has rough surface and un-uniform edge.
 The actual type of certificate that is issued will be dependent of the particular plate supplied, details of this certification are listed below.
The actual type of certificate that is issued will be dependent of the particular plate supplied, details of this certification are listed below.
The actual type of certificate that is issued will be dependent of the particular plate supplied, details of this certification are listed below.
EN10204:2004 3.1
This certificate is issued by the mill as a declaration of compliance with the specification and includes test results which are validated by the mill’s own in–house testing department. It is a requirement that this testing arrangement is completely separate and independent of the manufacturing centre.
EN10204:2004 3.2
A more demanding inspection where the steel is inspected not only by the mill but by a third party such as Lloyds Register or TUV. The third party will countersign the certificate which states that the plates are fully compliant with the specification and the test certificate is issued.
Magnetic Particle Inspection
Magnetic Particle Inspection (MPI) is a non-destructive testing method where an electrical current is passed through a test specimen forming a magnetic field.
The test is intended to establish if the continuity of the material is intact and identifies surface and near surface flaws. Once magnetised, if there is any discontinuity in the material, the magnetic field will leak. Iron particles are applied to the specimen and if an area of leakage is present the iron particles will be attracted to this area. The build up of these particles indicates potential flaws in the material which can then be investigated further.
Magnetic Particle Inspection is an excellent method for detecting surface or near surface cracks in the material. The specimen should be tested in two directions at 90 degrees because it is possible that a surface crack could be following the direction of the magnetic field. If this were the case the field is unlikely to be interrupted and therefore no flaw would be identified.
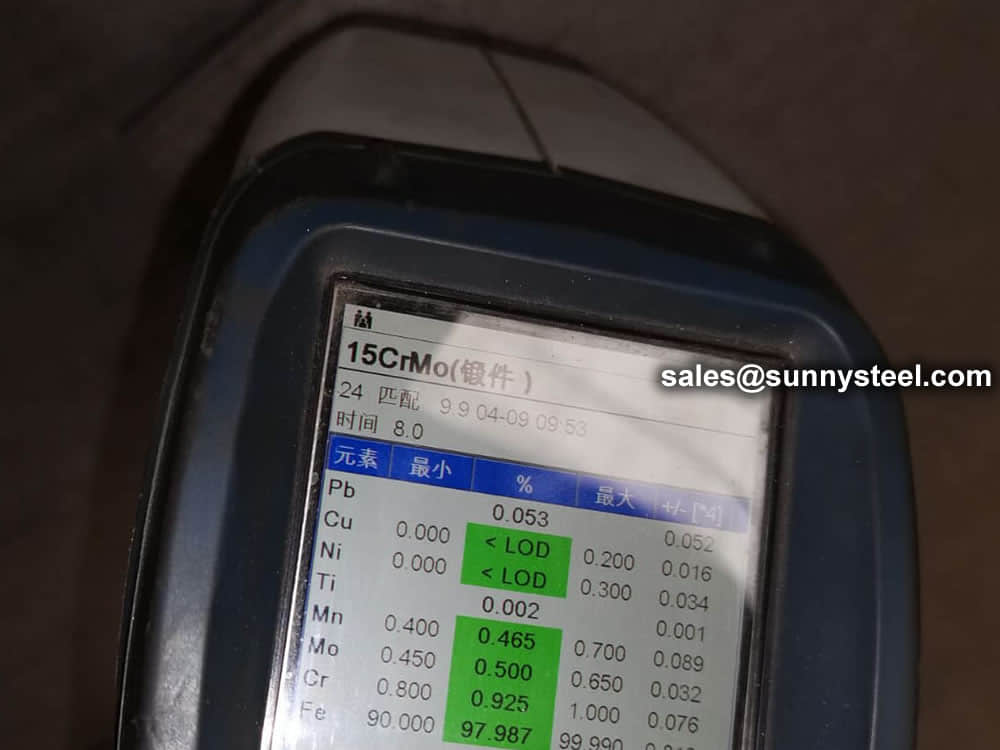
PMI test
To ensure the accuracy of the material. Positive Material Identification (PMI) of stainless steel sheets for tube shields is critical to verifying the grade and composition of stainless steel before it goes into production.
Carbon (C) :
1. Improve the deformation resistance and tensile strength of the blade;
2. Enhance hardness and improve wear resistance.
Cr (Cr) :
1. Enhance hardness, tensile strength and toughness;
2. Anti-wear and corrosion.
Cobalt (CO) :
1. Increase the hardness and strength so that it can withstand high temperature quenching;
2. Used to enhance certain individual properties of other elements in more complex alloys.
Copper (Cu) :
1. Enhance corrosion resistance;
2. Enhance wear resistance.
Manganese (Mn) :
1. Increase the quenchability, wear resistance and tensile strength;
2.Removal of oxygen from molten metal by separate oxidation and separate vaporization;
3. When added in large quantities, the hardness is enhanced, but the brittleness is improved.
Molybdenum (Mo) :
1. Enhanced strength, hardness, quenchability and toughness;
2. Improve machinability and corrosion resistance.
Nickel (Ni) :
1. Enhance strength, hardness and corrosion resistance.
Phosphorus (P) :
Enhanced strength, machinability and hardness.
2. When the concentration is too large, it is easy to crack
Silicon (Si) :
1. enhanced ductility;
2. Increase the tensile strength;
3. Removal of oxygen from molten metal by separate oxidation and separate vaporization.
Sulphur (S) : small amount used to improve machinability.
Tungsten (W) : Increases strength, hardness and toughness.
Vanadium (V) : Increases strength, hardness and seismic resistance.
 According to requirements of customers, steel plates, steel pipes and other steel products supplied here can be delivered at the following states:
According to requirements of customers, steel plates, steel pipes and other steel products supplied here can be delivered at the following states:
No extra heat treatment to steel product after hot rolling or forging, steel plate or pipe is directly delivered after cooling, called hot rolled or hot forging. Final temperature range of the steel product is 800 ~ 960 ℃, generally cooled naturally in the air.
Hot rolling status is simply as normalizing treatment. The difference is that hot rolled final temperature is not steady, while normalizing is more strict at fire heating temperature control, the fluctuations of microstructure and properties of steel is bigger than normalizing.
Steel product produced by cold drawing, cold rolling or other cold forming process, could be directly delivered without any heat treatment is known as the cold drawn or cold rolled condition. Compared with the state of hot rolling, forging.
Cold drawing (rolling) state has the advantages of high dimensional accuracy, good surface quality, and have higher mechanical properties. But for steel surface has no oxidation skin coverage for steel product at cold drawing (rolling) delivery status, and has higher internal stress, it is vulnerable to corrosion or rust, so packaging, storage and transportation requires more strict conditions for steel plate or steel pipe of this delivery state, generally use warehouse storage, and temperature and humidity should be controlled within a normal range.
Normalize heat treatment temperature (hypo eutectoid steel: Ac3+30 to 50 °C, eutectoid steel: Accm+30 to 50 °C), temperature control is more strict than hot-rolled state, it has uniform performance.
Normalized state,compared with annealed state, due to rapid cooling process of normalizing, the number of pearlite in the microstructure of the steel increased, so it has higher comprehensive mechanical properties and can improve the low carbon steel of the widmanstatten structure and eutectoid cementite network form, it is used to prepare for further heat treatment.
Carbon steel, alloy steel are usually produced at normalizing delivery condition. Some high strength low alloy steel such as 14MnMoVBRE, 14CrMnMoVB steel, in order to obtain Bainite microstructure, also requires normalizing delivery condition.
The purpose of annealing is mainly to eliminate the legacy of tissue defects and improve internal stress, it’s the pre-treatment for better organization and performance for after processes.
Alloy structural steel, cold heading steel, bearing steel, tool steel, turbine blade steel, heat resistant stainless steel steel products are commonly used annealing state delivery.
High tempering temperature is conducive to eliminate internal stress, improve the plasticity and toughness of carbon structure steel, alloy steel; quench hardenability structural steel are adopted with high temperature tempering state delivery.
Some high strength martensite stainless steel, high-speed tool steel and high strength alloy steel, high temperature tempering is often after quenching (or drawing) process, steel product of this delivery state has good machinability.
Solid Solution State is mainly applied to the treatment of austenitic stainless steel. Single-phase austenite is obtained through solid solution treatment, in order to improve the toughness and plasticity of the steel, also prepare for further cold rolled or cold drawn processing.
 And for further peace of mind, we ensure that your steel consignment is tested to your requirements. Much of our steel stock is “pre–tested” to an extremely stringent level so in most cases it is available to ship immediately. For direct supply from the mill, we can arrange for your steel to be tested at source or you can arrange for a third party company to complete the testing – the choice is yours.
And for further peace of mind, we ensure that your steel consignment is tested to your requirements. Much of our steel stock is “pre–tested” to an extremely stringent level so in most cases it is available to ship immediately. For direct supply from the mill, we can arrange for your steel to be tested at source or you can arrange for a third party company to complete the testing – the choice is yours.
Each package is fitted with an adhesive label with the following standard information:
Material standards
Material testing type (EN10204-3.1 / 2.2 …)
Dimensions of the steel plate
Number of the steel sheets that make up the package
Package weight
Package number (package ID)
Purchase order confirmation number
Client order number
Destination address
Material quality
Lot
Specimen
Upon request it is possible to customize the writing on the label, and if agreed, place additional labels on the packages. 
Need to inquire about our products? Fill out the form below and our staff will be in touch!
Q: How long is your delivery time? A: The delivery time of customized products is generally 25 35 days, and non customized products are generally shipped within 24 hours after payment. Q: Do you provide samples? Is it free? A: If the value of the sample is low, we will provide it for free, but the freight needs to be paid by the customer. But for some high value samples, we need to charge a fee. Q: What are your payment terms? A: T/T 30% as the deposit,The balance payment is paid in full before shipment Q: What is the packaging and transportation form? A: Non steaming wooden box and iron frame packaging. Special packaging is available according to customer needs. The transportation is mainly by sea. Q: What is your minimum order quantity? A: There is no minimum order quantity requirement. Customized products are tailor made according to the drawings provided by the customer.